Vol. 71, No. 9 (2022)
2022-05-05
SPECIAL TOPIC—Terahertz spintronic optoelectronics

EDITOR'S SUGGESTION
2022, 71 (9): 090702.
doi:10.7498/aps.71.20201139
Abstract +
Since the discovery of the ultrafast demagnetization of the ferromagnetic metal, the spin degree of electrons is gradually used to generate terahertz radiation. The terahertz radiation generated by the inverse Rashba-Edelstein effect was confirmed first at the interface of Ag/Bi. However, the spin-to-charge conversion efficiency of the LaAlO3/SrTiO3interface is one order of magnitude lager than that of the Ag/Bi interface under equilibrium or quasi-equilibrium condition. Whether the LaAlO3/SrTiO3heterostructures can be used to convert spin current to generate terahertz radiation remains to be systemically studied. In this work, we fabricate the NiFe/LaAlO3//SrTiO3heterostructures and investigate the generation of terahertz radiation by femtosecond laser pumping and its dependence of the magnetic field direction. We change the thickness of the LaAlO3to show the applicability of the superdiffusive spin transport model and optical transmission model. We find the multireflections at the LaAlO3/SrTiO3interface weaken the terahertz radiation intensity. This work provides experimental and theoretical support for further optimizing the generation of terahertz electromagnetic waves.
REVIEW
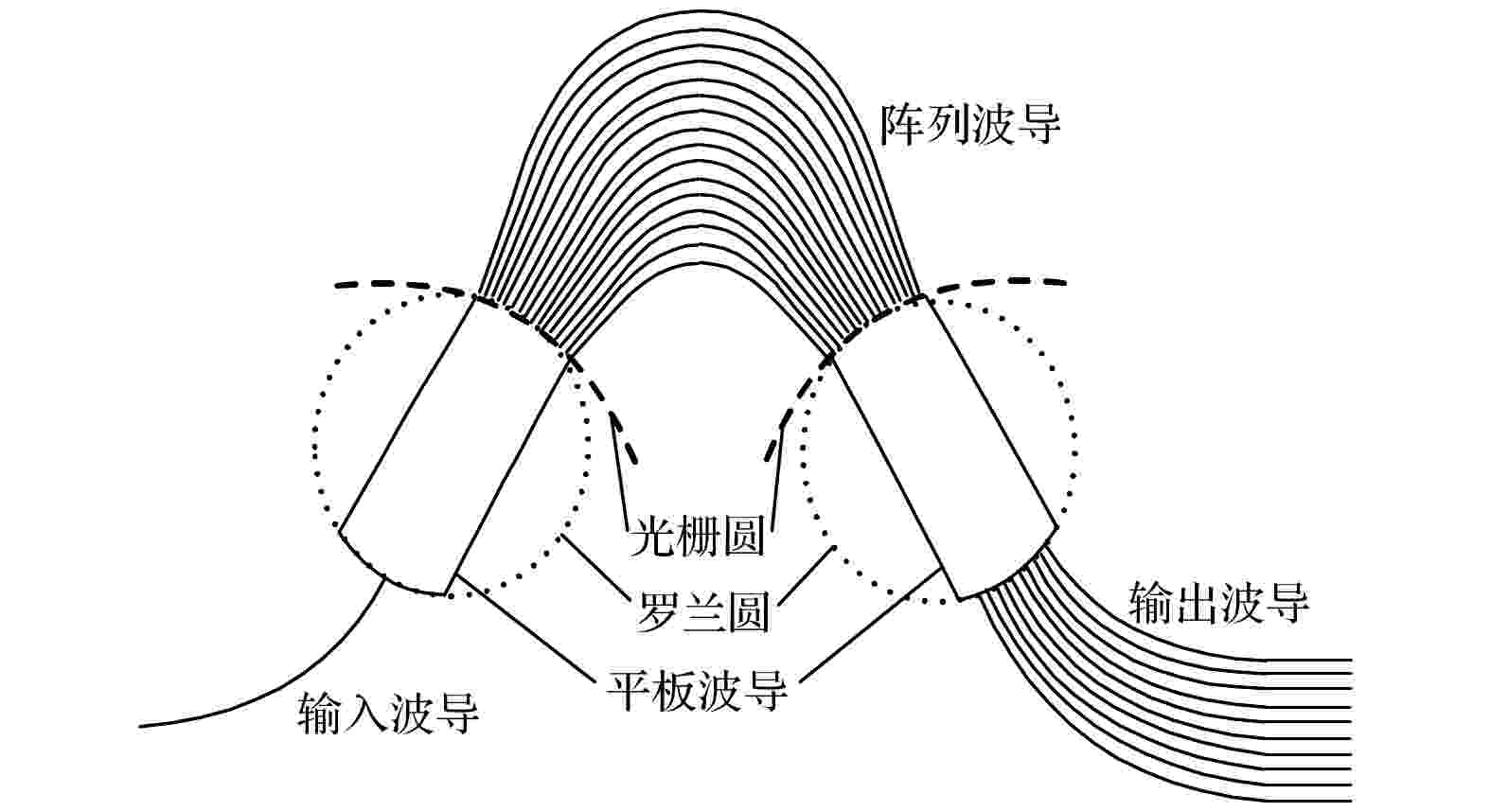
2022, 71 (9): 094207.
doi:10.7498/aps.71.20212063
Abstract +
The photonic integrated interrogation technology based on array waveguide grating is a hot but difficult research area in the silicon optical field. Compared with traditional interrogation methods, the photonic integration interrogation technology based on an array waveguide grating has obvious advantages in high-speed and high-precision demodulation of fiber Bragg gratings due to its high demodulation accuracy, fast demodulation speed, and small package size. In recent years, with the development of photonic integration technology, various research institutions and relevant organizations have conducted extensive and in-depth research and optimization on the photonic integration interrogation method of array waveguide gratings. In this paper we introduce the working principle of array waveguide grating and the principle of fiber Bragg grating wavelength interrogation based on array waveguide grating, the important progress of fiber Bragg grating interrogator based on array waveguide grating in both material system and system performance, and summarize the typical applications in interrogator based on array waveguide grating. The future development of fiber Bragg grating demodulation system is proposed from three aspects: new materials, system integration, and scale-up, which provides a reference for the research and development of photonic integrated interrogation technology based on array waveguide grating.
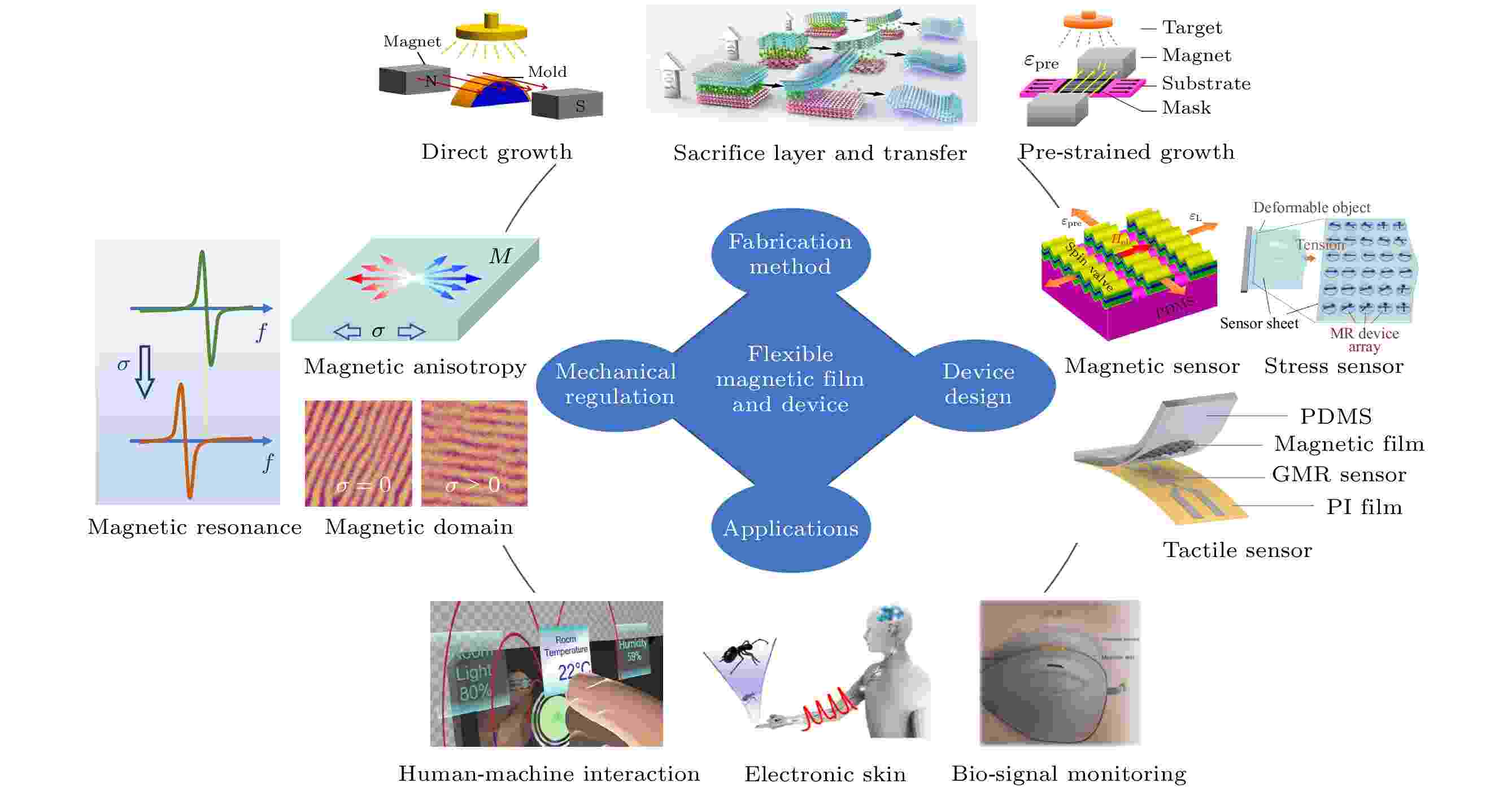
2022, 71 (9): 097503.
doi:10.7498/aps.71.20212354
Abstract +
With the rise of the internet of things, humanoid robots, and mobile healthcare services, etc., flexible electronic materials and devices have received extensive attention. Sensors and memories based on magnetic materials are important components of electronic devices. With the development of flexible film material preparation technology, one has prepared high-quality flexible and even stretchable magnetic metal and oxide films, which exhibit not only greater deformation capability, but also new physical effects and responses. Most recent studies show that flexible magnetoelectronic devices are advantageous in non-contact sensing, highly sensitive strain detection, and super-resolution tactile sensing, showing their broad application prospects. In this work, the research progress of this emerging field is reviewed from the aspects of the preparation of flexible magnetic materials, the regulation of physical properties and the applications of devices, and the future development trend is also presented.
GENERAL
2022, 71 (9): 090301.
doi:10.7498/aps.71.20212168
Abstract +
In this paper, we study the interaction-modulated tunneling dynamics of a Bose-Fermi superfluid mixture, where a Bose-Einstein condensate (BEC) with weak repulsive interaction is confined in a symmetric deep double-well potential and an equally populated two-component Fermi gas in a harmonic potential symmetrically is positioned in the center of the double-well potential. The tunneling between the two wells is modulated by fermions trapped in a harmonic potential. When the temperature is adequately low and the bosonic particle number is adequately large, we can employ the mean-field theory to describe the evolution of the BEC in the double-well potential through the time-dependent Gross-Pitaevskii equation. For the Fermi gas in the harmonic potential trap, we consider the case where the inter-fermion interaction is tuned on the deep Bose-Einstein condensate of the inter-fermion Feshbach resonance, where two fermions of spin-up and spin-down form a two-body bound state. Within the regime, the Fermi gas is well described by a condensate of these fermionic dimers, and hence can be simulated as well by a Gross-Pitaevskii equation of dimers. The inter-species interactions couple the dynamics of the two species, which results in interesting features in the tunneling oscillations. The dynamic equations of the BEC in the double-well potential is described by a two-mode approximation. Coupling it with time-dependent Gross-Pitaevskii equation of the harmonically potential trapped molecular BEC, we numerically investigate the dynamical evolution of the Boson-Fermi hybrid system under different initial conditions. It is found that the interaction among fermions in a harmonic potential leads to strong non-linearity in the oscillations of the bosons in the double-well potential and enriches the tunneling dynamics of the bosons. Especially, it strengthens macroscopic quantum self-trapping. And the macroscopic quantum self-trapping can be expressed in three forms: the phase tends to be negative and monotonically decreases with time, the phase evolves with time, and the phase tends to be positive and increases monotonically with time. This means that it is possible the tunneling dynamics of the BEC in double-well potential is adjustable. Our results can be verified experimentally in a Bose-Fermi superfluid mixture by varying different interaction parameters via Feshbach resonance and confinement-induced resonance.
2022, 71 (9): 090501.
doi:10.7498/aps.71.20211474
Abstract +
Multi-physics coupling calculation has applications in many important research fields. If particle transport process is included in this calculation, Monte Carlo method is often used to simulate this process and usually a large amount of calculation time is needed. So, efficient Monte Carlo algorithm for time-dependent particle transport problem is important for an efficiently coupling calculation, which inevitably relies on large-scale parallel calculation. Based on the characteristic of time-dependent particle transport problem, two methods are proposed in this paper to achieve high- efficiency calculation. One is a tally-reducing algorithm which is used in the coupling of transport simulation and burnup calculation. By reducing the quantity of data which should be reduced necessarily, this method can reduce the calculation time largely. It can be seen that a new coupling mode for these two processes in MPI environment has a larger value when model scale is larger than the sample size. The other method is an adaptive method of setting the sample size of Monte Carlo simulation. The law of large number assures that the Monte Carlo method will obtain an exact solution when the sample scale tends to infinity. But generally, no one knows which sample scale is big enough for obtaining a solution with target precision in advance. So, the common strategy is to set a huge-enough sample scale by experience and conduct the posterior check for all results. Apparently, this way cannot be efficient because the calculation will go on after the precision of solution has reached an object value. Another popular method is to set the sample size to rely on the relative error of some single calculation. The sample size is enlarged without a break until the relative error is less than some presetting value. This method is not suitable either, because Monte Carlo particle transport simulation will gives feedbacks to other process which is composed of many tallies. It is inappropriate to adjust the sample size according to the relative error of any calculation. Relying on the generalization of the Shannon entropy concept and an on-the-fly diagnosis rule for a entropy value sequence, the adaptive method proposed in this paper can reduce the original huge sample scale to a reasonable level. By numerically testing some non-trivial examples, both algorithms can reduce the calculation time largely, with the results kept almost unchanged, so the efficiency is high in these cases.
2022, 71 (9): 090601.
doi:10.7498/aps.71.20212029
Abstract +
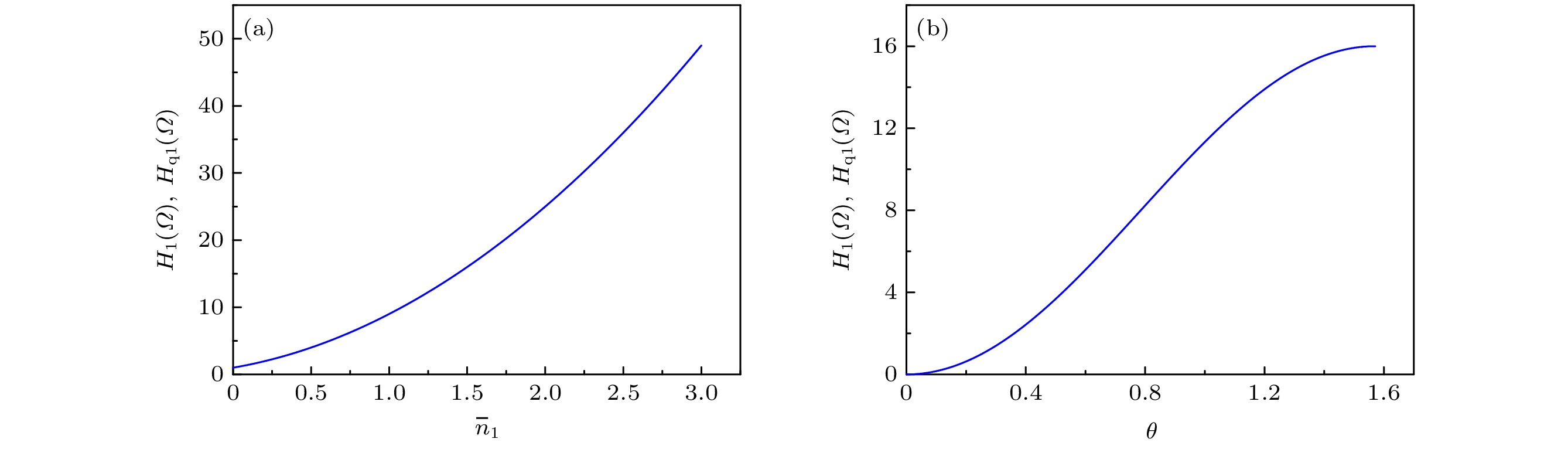
Quantum parameter estimation is one of the most important applications in quantum metrology. The basic theory of quantum parameter estimation-quantum Cramer-Rao bound-shows that the precision limit of quantum parameter estimation is directly related to quantum Fisher information. Therefore quantum Fisher information is extremely important in the quantum parameter estimation. In this paper we use quantum parameter estimation theory to estimate the coupling constant of the Jaynes-Cummings model with large detuning. The initial probing state is the direct product state of qubit and radiation field in which Fock state, thermal state and coherent state are taken into account respectively. We calculate the quantum Fisher information of the hybrid system as well as qubit and radiation field for each probing state after the parameter evolution under the Hamiltonian of the Jaynes-Cummings model with large detuning. The results show that the quantum Fisher information increases monotonically with the average photon number increasing. The optimal detection state is that when the qubit system is in the equal weight superposition of the ground and the excited state, at this time the quantum Fisher information always reaches a maximum value, When the radiation field of probing state is Fock state or the thermal state, the information about the estimated parameter is included only in the qubit. The estimation accuracy of the coupling constant with thermal state or coherent state is higher than that with Fock state.
2022, 71 (9): 090602.
doi:10.7498/aps.71.20212073
Abstract +
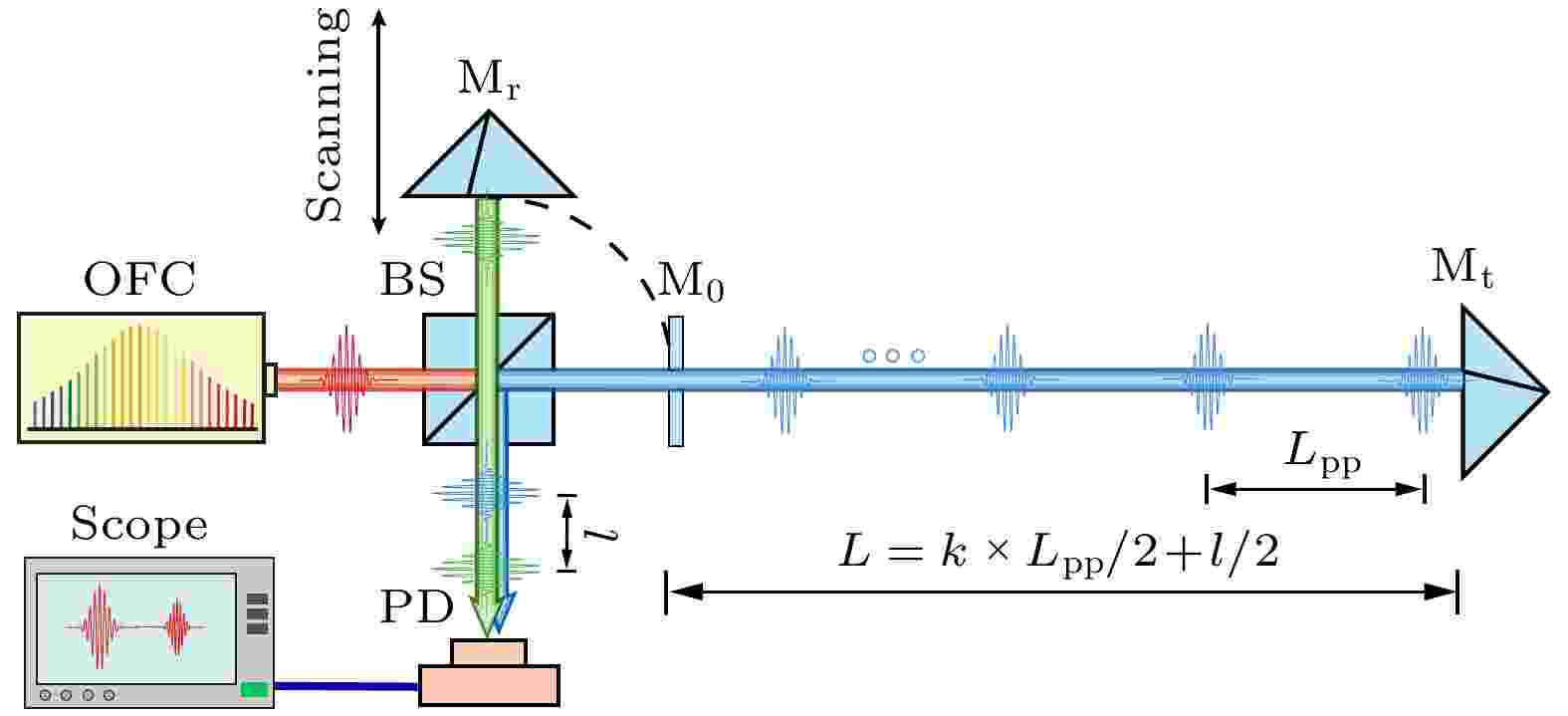
In this paper, the Fabry-Perot etalon is used to multiply the repetition rate of the fiber optical frequency comb. The repetition rate is amplified from 250 MHz to 10 GHz, and the corresponding pulse interval is reduced from 1200 mm to 30 mm. For the pulse cross correlation ranging method, the repetition rate multiplication can greatly reduce the length requirement of the scanning reference arm. We analyze in detail the principle of cross correlation interferometry based on repetition rate multiplication frequency comb. A numerical mode of the function is comprehensively established. The basic parameters of optical source and Fabry-Perot cavity for the influence of filtered optical spectrum and cross correlation fringe are analyzed through the numerical simulation. The multiplied frequency comb is utilized for absolute ranging with the help of a pulse cross correlation method. By comparison, our result differs from the result obtained by a conventional counting interferometer only by 4 μm for distances up to 210 mm.
2022, 71 (9): 090701.
doi:10.7498/aps.71.20212195
Abstract +
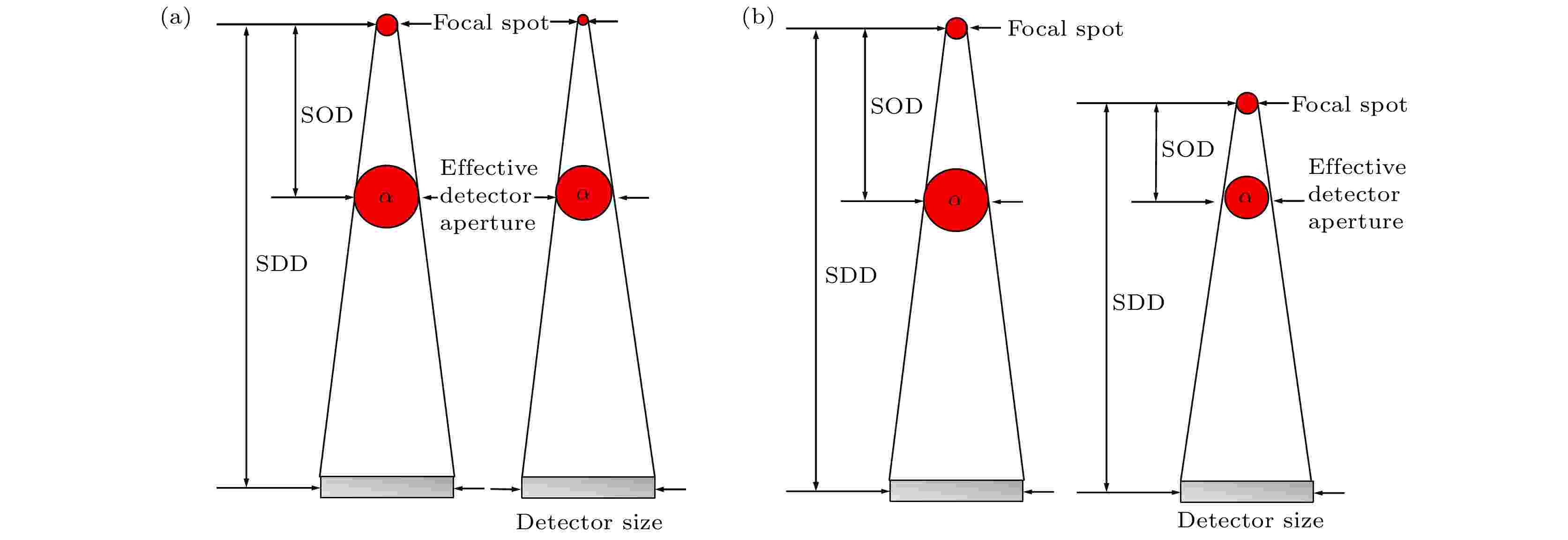
In-vivosmall animal imaging system is an important part of disease research and new drug development. It is essential for living small animal imaging system to be able to provide the anatomical structure, molecular and functional information. The X-ray micro cone-beam computed tomography (micro-CBCT) can perform longitudinal study with a resolution of tens-to-hundreds of microns in a short imaging time at a relatively low cost. Furthermore, it is easy to combine with other modalities to provide abundant information about small animals. A key challenge to the micro-CBCT scanner is that its spatial and contrast resolution determined primarily by the X-ray focal spot size, the detector element size, and the system geometry. Aiming to improve the spatial resolution, contrast resolution, and imaging uniformity of the micro-CBCT system, we use the X-ray polycapillary optics for adjusting the X-ray source. A micro-CBCT based on X-ray polycapillary optics with a large field of view is constructed for the small animal imaging study. The micro-CBCT system is composed of microfocus X-ray tube with an attached polycapillary focusing X-ray lens, amorphous silicon-based flat panel detector, rotation stage, and controlling PC. The Feldkamp-Daivs-Kress (FDK) algorithm is adopted to reconstruct the image. The system performances are evaluated. The magnification of this micro-CBCT system is 1.97. The results show that the spatial resolution of the system at 10% modulation transfer function (MTF) is 9.1 lp/mm, which is 1.35 times higher than that in the case of no optics. The image uniformity deterioration caused by hardening effect is effectively alleviated by filtrating the low energy X-rays with the X-ray polycapillary optics and the contrast enhancement is more than twice. The anesthetic rats are imaged with this micro-CBCT systemin vivoand the practicability of the system in small animal imaging research is verified.
THE PHYSICS OF ELEMENTARY PARTICLES AND FIELDS
2022, 71 (9): 091401.
doi:10.7498/aps.71.20211653
Abstract +
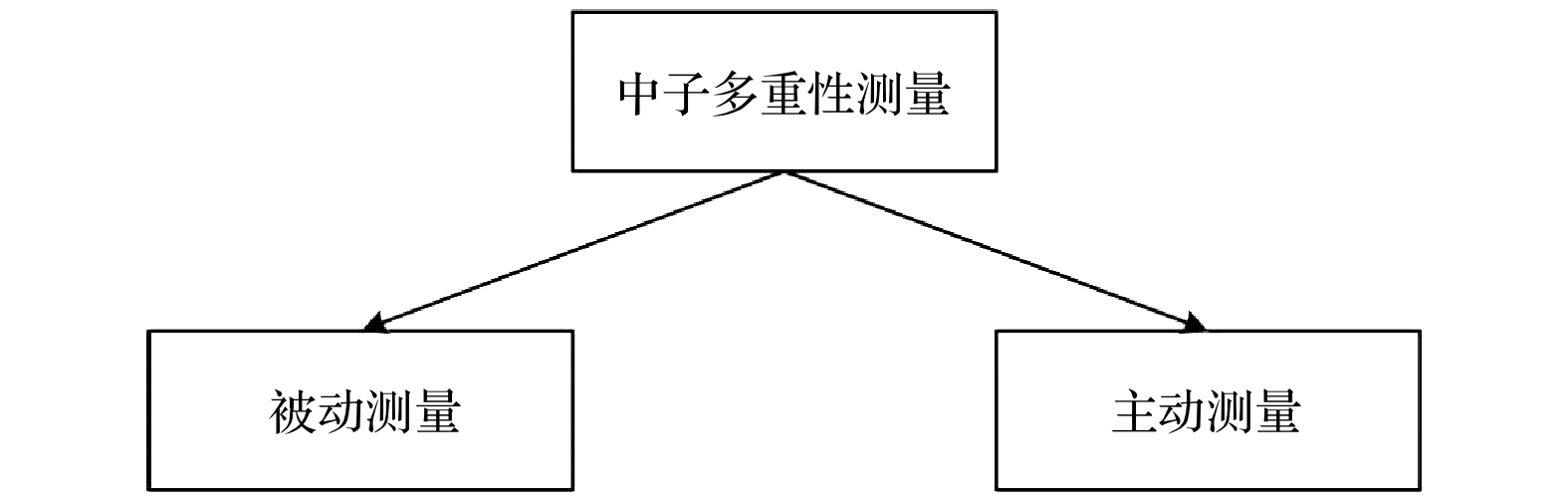
With the deepening of international nuclear disarmament, attribute certification for nuclear material has attracted more and more attention. The fast neutron multiplicity measurement technology-a non-destructive testing method-uses scintillator detector for measurement, which plays a more and more important role in the military control verification system. At present, the fast neutron multiplicity measurement methods for plutonium materials are relatively mature, but the fast neutron multiplicity analysis model and measurement equations of uranium materials are still under development. In order to establish the active fast neutron multiplicity measurement equation for uranium materials, based on the derivation process of neutron multiplicity counting analysis equation, in this paper uses the probability generating function is used to derive the fast neutron multiplicity measurement equation of uranium materials according to the difference between the physical processes of uranium and plutonium materials, without considering the reaction of
$ (\alpha , n) $
or the influence of fast neutron scattering crosstalk. On this basis, in order to verify the validity of the measurement equation, Geant4 is used to build a 3 × 8 well-type detection system for simulation measurement. The fitting function relationship between the coupling coefficient and the value-added coefficient, the multiplicity counting rate, and the solution deviation of the quality are analyzed, thereby confirming the reliability and the accuracy of the measurement equation, which is of great significance in developing the fast neutron multiplicity technology.
ATOMIC AND MOLECULAR PHYSICS
EDITOR'S SUGGESTION
2022, 71 (9): 093101.
doi:10.7498/aps.71.20212108
Abstract +
Quantum calculation of molecular vibrational frequency is important in investigating infrared spectrum and Raman spectrum. In this work, a low computational cost method of calculating the quantum chemistry of vibrational frequencies for large molecules is proposed. Usually, the calculation of vibrational frequency of a molecule containingNatoms needs to deal with the Hessian matrix, which consists of second derivatives of the 3N-dimensional potential hypersurface, and then solve secular equations of the matrix to obtain normal vibration modes and the corresponding frequencies. LargerNimplies higher computational cost. Therefore, for a limited computational hardware condition, higher-level computations for largeNatomic molecule’s vibrational frequencies cannot be implemented in practice. Here we solve this problem by calculating the vibrational frequency for only one vibrational mode each time instead of calculating the Hessian matrix to obtain all vibrational frequencies. When only one vibrational mode is taken into consideration, the molecular potential hypersurface can be transformed into one-dimensional curve. Hence, we can calculate the curve with high-level computational method, then deduce the expression of one-dimensional curve by using harmonic oscillating approximation and obtain the vibrational frequency by using the expression to fit the curve. It should be noted that this method is applied to vibrational modes whose vibrational coordinates can be completely determined by equilibrium geometry and the molecular symmetry and be independent of the molecular force constants. It requires that there exists no other vibrational mode with the same symmetry but with different frequencies. The lower computational cost for a one-dimensional potential curve than that for 3N-dimensional potential hypersurface’s second derivatives permits us to use higher-level method and larger basis set for a given computational hardware condition to achieve more accurate results. In this paper we take the calculation ofB2vibrational frequency of water molecule for example to illustrate the feasibility of this method. Furthermore, we use this method to deal with the SF6molecule. It has 7 atoms and 70 electrons, hence there exists a large amount of electronic correlation energy to be calculated. The MRCI is an effective method to calculate the correlation energy. But by now no MRCI result of SF6vibrational frequencies has been reported. So here we use MRCI/6-311G* to calculate the potential curves of A1g, Eg, T2gand T2uvibrational modes separately, deduce their expressions, then use the expressions to fit the curves, and finally obtain the vibrational frequencies. The results are then compared with those obtained by other theoretical methods including HF, MP2, CISD, CCSD(T) and B3LYP methods through using the same 6-311G* basis set. It is shown that the relative error to experimental result of the MRCI method is the least in the results from all these methods.
2022, 71 (9): 093102.
doi:10.7498/aps.71.20211451
Abstract +
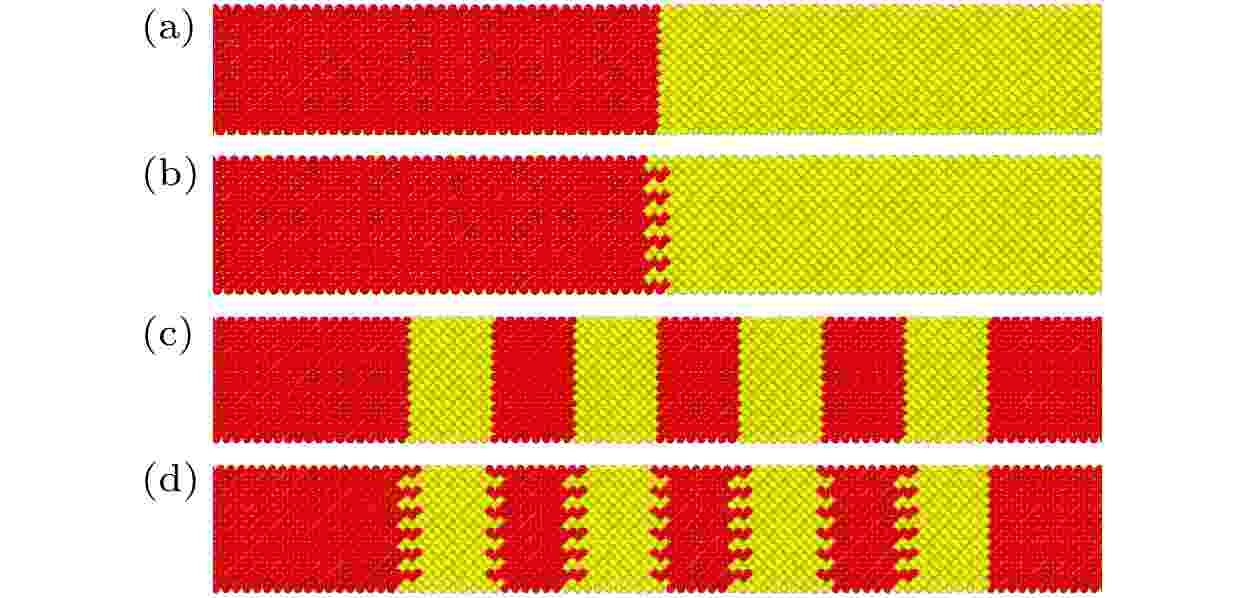
The Si/Ge single interface and superlattice structure with atom mixing interfaces are constructed. The effects of interfacial atomic mixing on thermal conductivity of single interface and superlattice structures are studied by non-equilibrium molecular dynamics simulation. The effects of the number of atomic mixing layers, temperature, total length of the system and period length on the thermal conductivity for different lattice structures are studied. The results show that the mixing of two and four layers of atoms can improve the thermal conductivity of Si/Ge lattice with single interface and the few-period superlattice due to the “phonon bridging” mechanism. When the total length of the system is large, the thermal conductivity of the superlattice with atomic mixing interfaces decreases significantly compared with that of the perfect interface. The interfacial atom mixing will destroy the phonon coherent transport in the superlattice and reduce the thermal conductivity to some extent. The superlattce with perfect interface has obvious temperature effect, while the thermal conductivity of the superlattice with atomic mixing is less sensitive to temperature.
2022, 71 (9): 093201.
doi:10.7498/aps.71.20212366
Abstract +
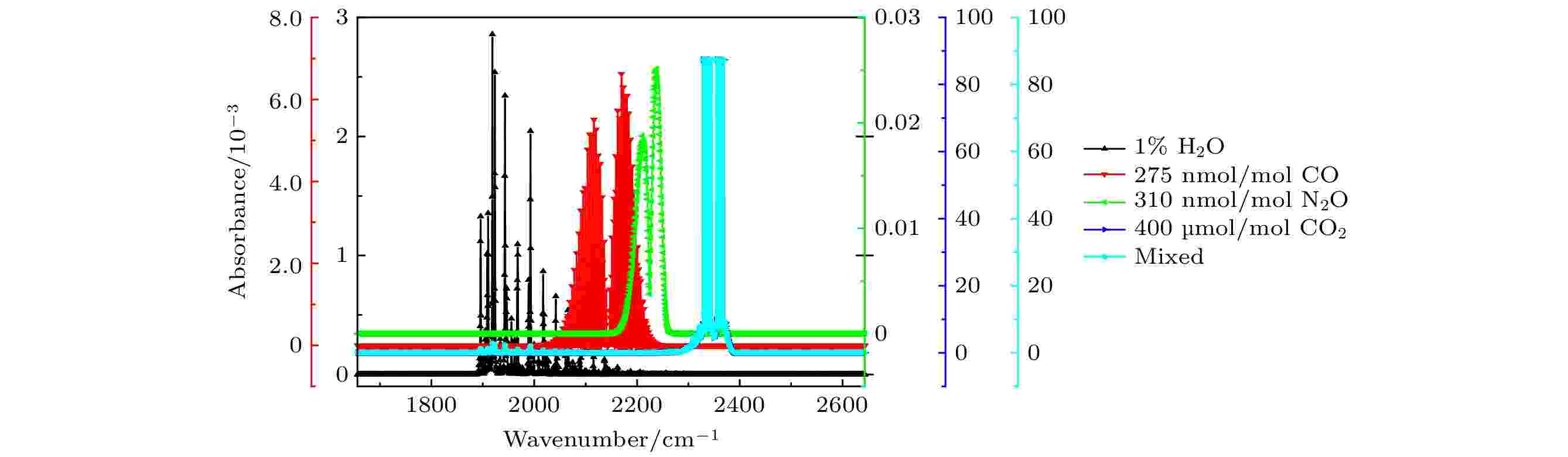
The minimum amount that can be detected and quantitatively analyzed by Fourier infrared spectrometer depends on the signal-to-noise ratio of the measured gas spectrum. In order to use Fourier transform infrared absorption spectroscopy to measure CO2, CO, CH4, N2O and other greenhouse gases, the signal-to-noise ratio and instrument detection limit of the mixed gas are studied. We propose a method to calculate the gas detection limit of the instrument through the HITRAN simulation spectrum. In addition, we build an experimental platform to verify the accuracy of the detection limit approximation based on the HITRAN simulation spectrum calculation, which serves as the actual measurement detection limit of the instrument, and we also analyze the reasons why there appears the error between the existing experimental platform and optimization scheme and their deficiencies as well.
2022, 71 (9): 093202.
doi:10.7498/aps.71.20212226
Abstract +
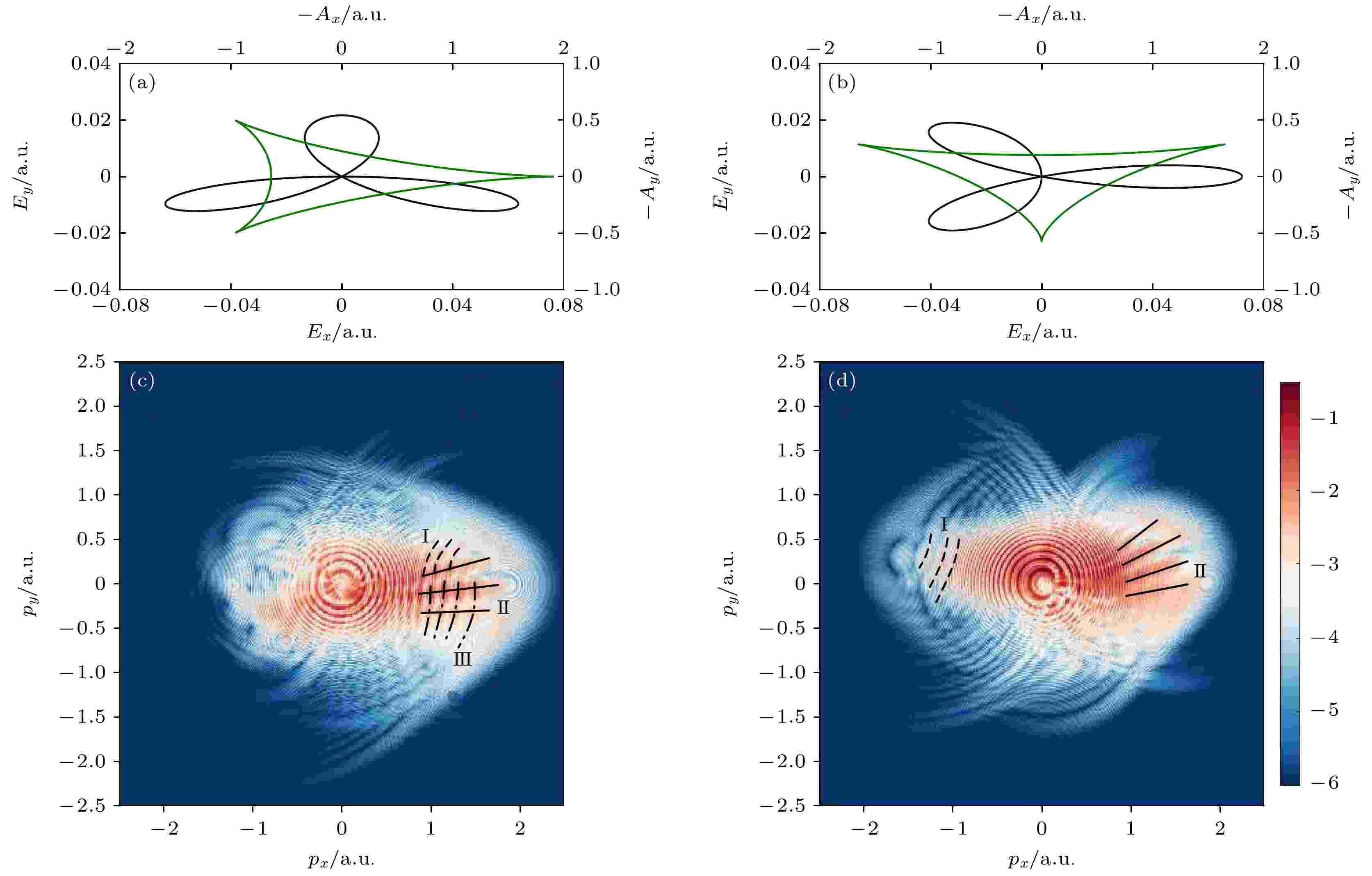
In this paper, photoelectron interference in tunneling ionization of atoms by counter-rotating two-color elliptically polarized (TCEP) laser fields are investigated by numerically solving the two-dimensional time-dependent Schrödinger equation (TDSE) and strong field approximation (SFA). When the ellipticities of the two pulses are both 0.3, for a relative phase of 0.25π, the intracycle interference, fork-like holographic interference and arc-like holographic interference in the photoelectron momentum distribution overlap with each other. For a relative phase of 0, the arc-like holographic interference disappears and the intracycle interference and fork-like holographic interference are fully separated into the –pxdirection and the +pxdirection. Furthermore, the independent fork-like holographic interference can be enhanced or suppressed by changing the ellipticities of the two pulses. This provides an efficient tool for controlling and separating the interference structures in the photoelectron momentum distribution, which facilitates extracting the information about the target structure and the photoelectron ultrafast dynamics in strong fields.
EDITOR'S SUGGESTION
2022, 71 (9): 093401.
doi:10.7498/aps.71.20212202
Abstract +
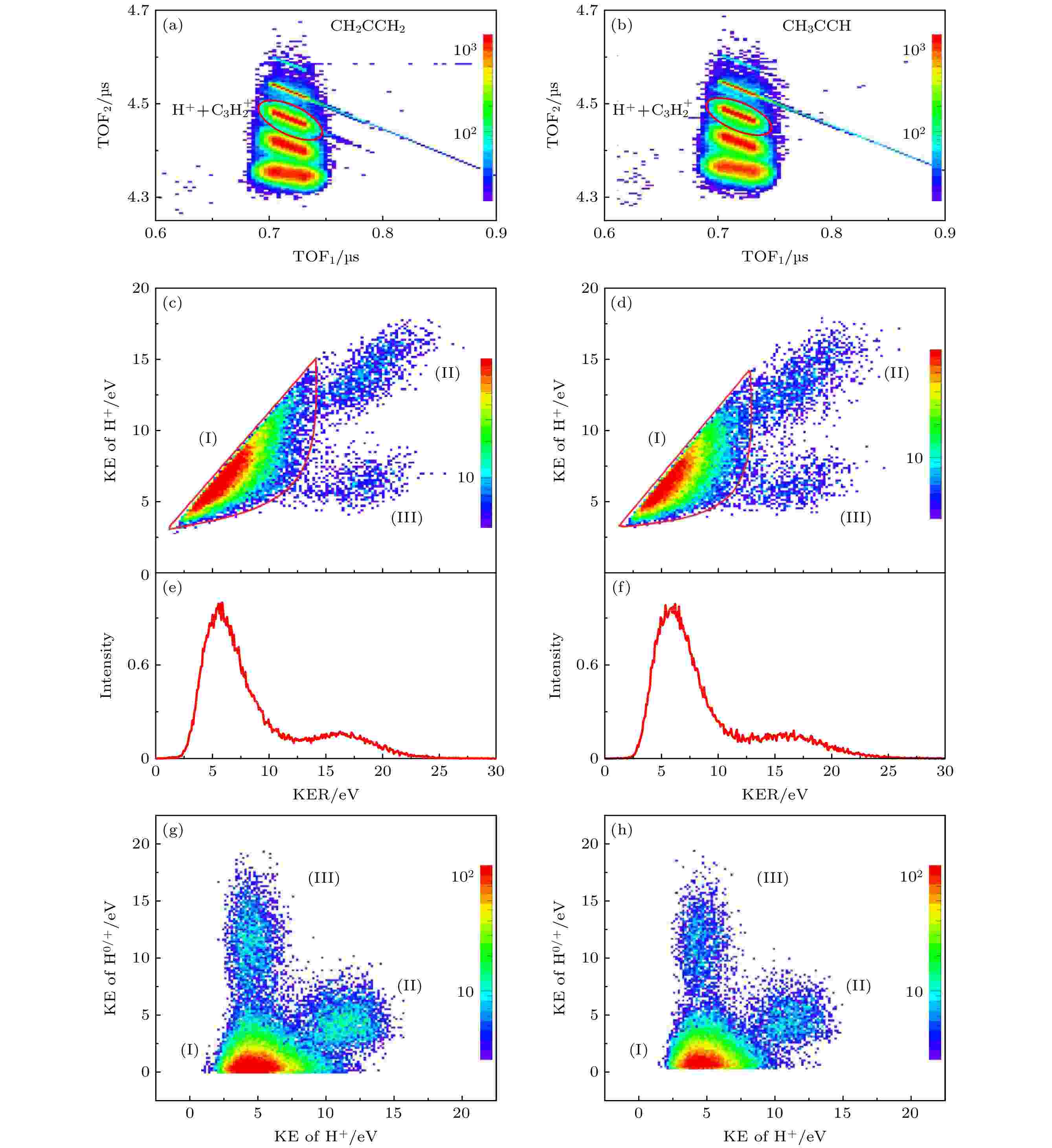
The experiment on collision between 50-keV/u Ne8+ion and C3H4molecule is carried out by reaction microscopic imaging spectrometer. The process of forming the
$\rm C_3H_4^{2+}$
divalent ion from propylene (CH2CCH2) and proacetylene (CH3CCH) and then dissociating to produce H+and C3H2+
$\rm C_3H_2^+$
ions and H atom is studied. Using the reaction microscope, the momentum vector of H+ion and the momentum vector of
$\rm C_3H_2^+$
ion are directly obtained, and then the momentum of the undetected fragment is reconstructed according to momentum conservation. By analyzing the kinetic energy of the three fragments and the total kinetic energy released from the dissociation process, the events with H atom as the third fragment are discriminated from H+, and thus the H+ion,
$ \rm C_3H_2^+ $
ion, and H atom are identified. In addition, it is found that the sequential fragmentation pathway in which H+ion and
$\rm C_3H_3^+$
ion are produced in the first step followed by dissociation of
$ \rm C_3H_3^+ $
into
$ \rm C_3H_2^+ $
ion and H atom in the second step is the dominant dissociation mechanism according to the detailed analyses of the Dalitz plot, Newton diagram andαdistribution.
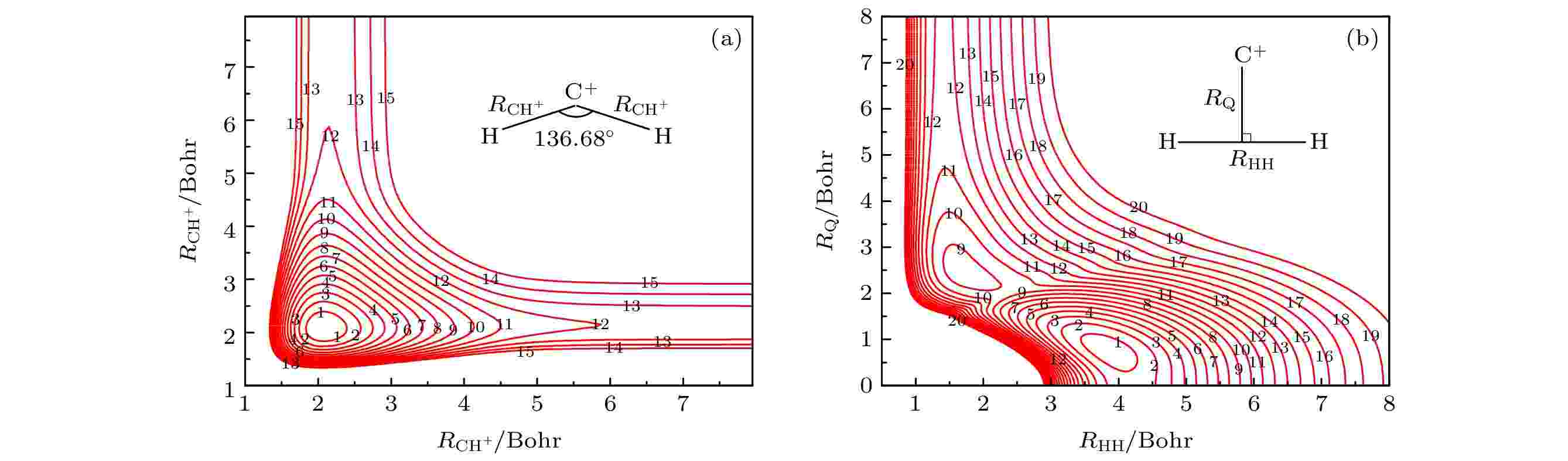
2022, 71 (9): 093402.
doi:10.7498/aps.71.20212241
Abstract +
The multi-reference interaction method is explicitly dependent on the electron-electron distance, and ACVQZ basis set is used in theab initiocalculation. The potential energy surface (PES) is fitted by using the permutation invariant polynomial neural network method based on 18222ab initiopoints. In addition, the topographical features of the PES are compared with available theoretical and experimental data. The results indicate that the present PES is more accurate and can be applied to any type of dynamic study. In order to validate the PES, the dynamic study of the C++ H2→ H + CH+reaction is carried out by using the quasi-classical trajectory method in a collision energy range of 0.4–1.0 eV. The integral cross sections and differential cross sections are calculated and compared with previous theoretical studies. For the integral cross section, the present results are, in general, in good agreement with previous theoretical studies, both of which increase with collision energy increasing. The forward and backward symmetric differential cross sections indicate that the “complex-forming” mechanism plays a dominant role in the reaction.
ELECTROMAGNETISM, OPTICS, ACOUSTICS, HEAT TRANSFER, CLASSICAL MECHANICS, AND FLUID DYNAMICS

2022, 71 (9): 094201.
doi:10.7498/aps.71.20211977
Abstract +
Hardmard transfer imaging spectrometer (HTIS) is a novel computationally optical system. Its characteristic of multi-channel multiplexing increases the luminous flux of the optical system without sacrificing spatial resolution, thereby enabling the system’s signal-to-noise ratio to be significantly higher than traditional spectrometer’s. Encoding with digital mirror devices (DMD) in the system causes a serious diffraction effect that gives rise to the apparent degradation of the imaging formation. For improving the image quality and spectral accuracy of the reconstructed data cube, the Hadamard coded spectral imaging data degradation model is established based on the scalar diffraction theory. A data reconstruction algorithm is proposed based on the Lucy Richardson (L-R) algorithm. Through the simulation experiment, the process of image degradation is revealed. On the one hand, it proves that the degradation of system imaging diffraction is the main reason for the distortion of reconstructed data. On the other hand, it verifies the effectiveness of the correction method adopted in this paper. The evaluation result of the spectral angle distance of the restored data cube after L-R correction is 0.1296, and the image similarity evaluation factor is better than 0.85. Compared with the reconstructed data before being corrected, the corrected data is greatly improved in quality. The experimental results show that the algorithm has a good correction effect on the data cube reconstruction of HTIS.
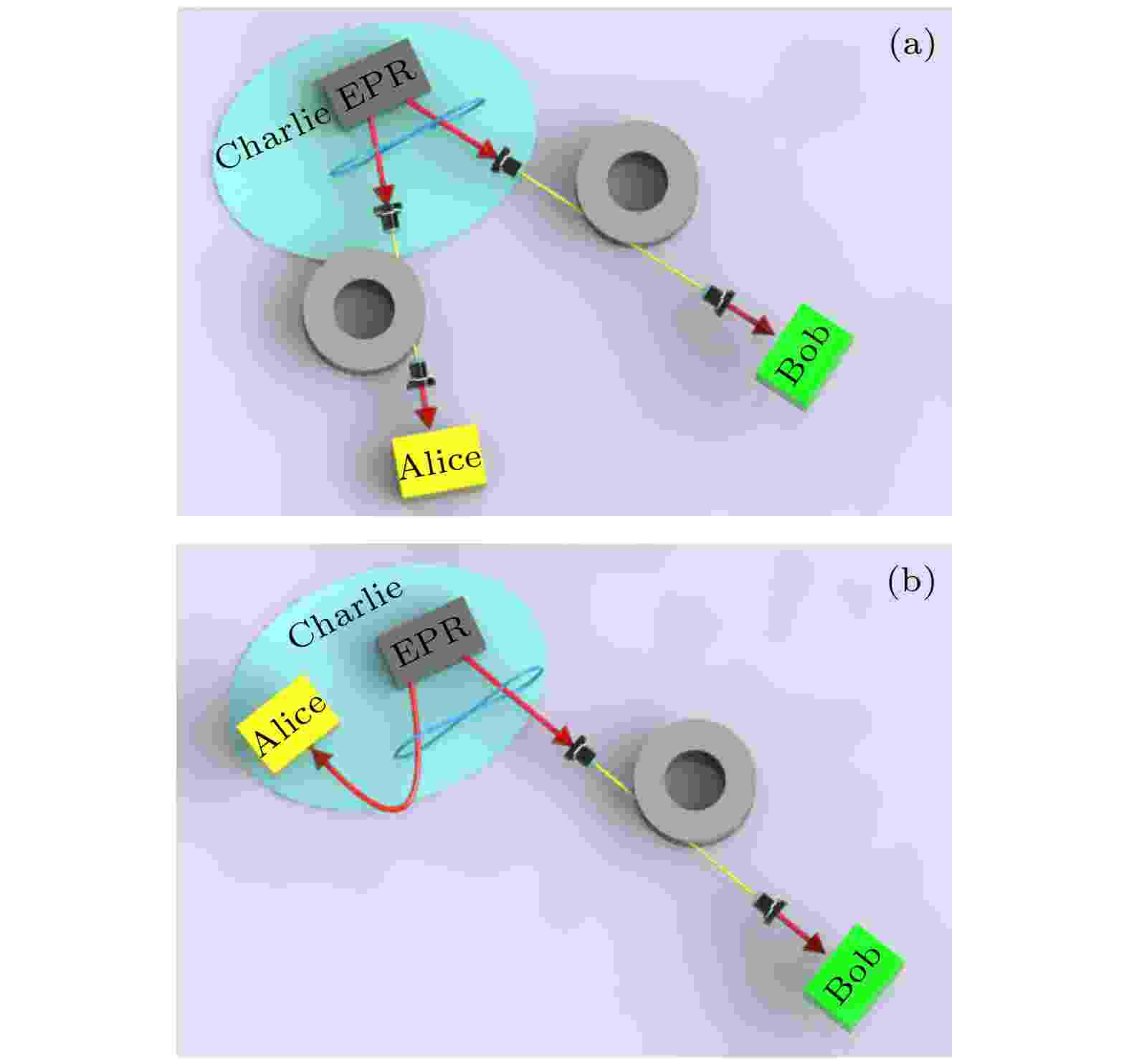
EDITOR'S SUGGESTION
2022, 71 (9): 094202.
doi:10.7498/aps.71.20212380
Abstract +
Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen (EPR)-entangled state light field at a telecommunication wavelength of 1.5 μm is an important quantum source for realizing the continuous variable quantum information processing and some quantum protocols over optical fiber channel. When the EPR-entangled state light field is distributed over the optical fiber channel, the disentanglement is always present because the the EPR entangled state interacts with the fiber channel. It affects the performance of quantum information processing. In this paper, we theoretically calculate the positive partial transposition (PPT) of the entangled state distributed over the optical fiber channel in the single-channel and dual-channel distribution scheme, respectively. Three types of initial entangled light field are considered and analyzed, they being an initial EPR entangled state, an EPR entangled state with asymmetric quadratures, and an EPR entangled state with asymmetric modes. Furthermore, the influence of the extra noise in the optical fiber on the transmission distance of EPR entangled state over the optical fiber channel is investigated. In the single-channel scheme or dual-channel scheme, the extra noise in the optical fiber channel leads the entangled state light field to be disentangled, and the transmission distance of EPR entangled state over the optical fiber channel to decrease rapidly with the increase of the extra noise. For maintaining the robustness of EPR entangled states in lossy optical fiber channels, the dual-channel scheme has more stringent requirements for the correlation quadrature symmetry and purity of the initial entangled state than the single-channel scheme. In the single fiber noise channel scheme, the maximum transmission distance and the robustness of the EPR entangled states with asymmetric modes are not sensitive to the asymmetry between modes. The change of asymmetry between modes does not lead to being disentangled. The maximum transmission distance does not change either. However, the decrease of asymmetry between modes results in the disentanglement in the double fiber noise channels’ scheme. The maximum transmission distance is reduced and the sudden death occurs to the entanglement. The present results will lay a foundation for continuous variables quantum information processing based on optical fiber, such as realizing continuous variables quantum communication over optical fiber and constructing metropolitan quantum network over optical fiber.

2022, 71 (9): 094203.
doi:10.7498/aps.71.20211727
Abstract +
Orthogonally-polarized dual-wavelength laser has significant practical applications in various fields, such as precision metrology, terahertz radiation generation, differential radar, spectral analysis. The Nd:YLF crystal has two orthogonally-polarized emission peaks with comparable emission cross sections, high-energy storage capability and relatively weak thermal lens effect. Owing to these properties, it has been recognized as a suitable gain medium for generating orthogonally-polarized dual-wavelength laser. In this paper, the Nd:YLF crystal with low doping concentration is employed as a laser gain medium to produce 1047 nm and 1053 nm dual-wavelength fundamental lasers with orthogonal polarizations, and the risk of thermal cracking of Nd:YLF crystal is reduced by appropriately increasing the pump spots. Using the intracavity Raman frequency shift in BaWO4crystal, orthogonally-polarized dual-wavelength Raman lasers at 1159.9 nm and 1167.1 nm are achieved to have high peak power. Under the total incident pump power of 40 W and a pulse repetition rate of 5 kHz, the maximum dual-wavelength Raman output power is obtained to be 2.67 W. The corresponding total optical conversion efficiency is 6.7%. For 1159.9 nm and 1167.1 nm Raman laser, their maximum average output power values are 1.31 W and 1.36 W, respectively. Their narrowest pulse widths are 1.50 ns and 1.53 ns, and the corresponding peak power values are as high as 174.7 kW and 177.8 kW, respectively. The results show that the problem of thermal cracking of Nd:YLF crystal at high pump power can be solved by reducing the doping concentration and increasing the pump spot. The Nd:YLF/BaWO4is a promising crystal combination for realizing orthogonally-polarized dual-wavelength Raman laser.
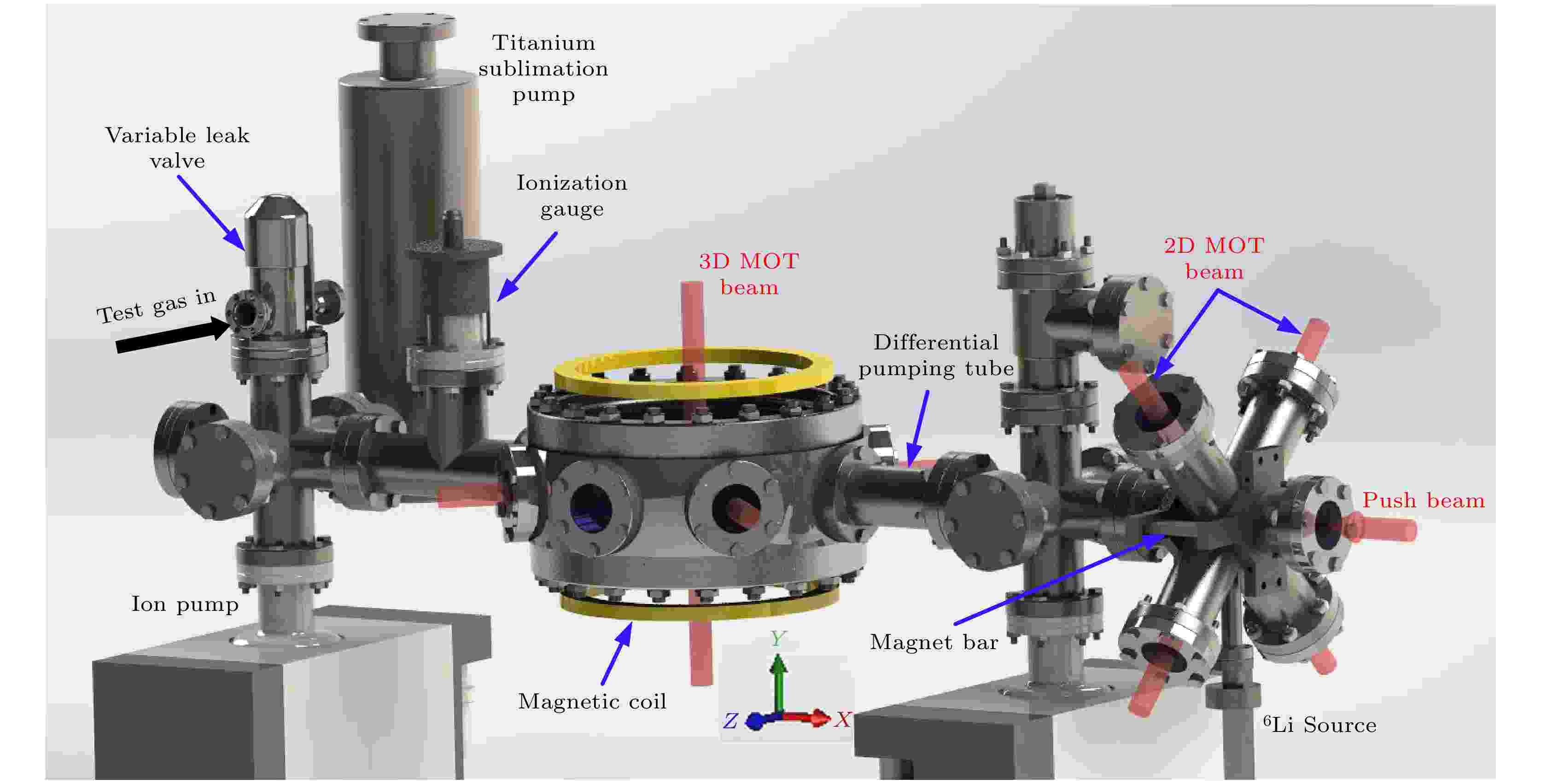
2022, 71 (9): 094204.
doi:10.7498/aps.71.20212204
Abstract +
Ultra-high vacuum measurement and extremely high vacuum (UHV/XHV) measurement play an important role in high-tech fields such as deep space exploration, particle accelerators, and nanoscience; with the continuous extension of the lower limit of measurement, especially when it reaches the order of 10–10Pa, higher requirements are placed on the accuracy of the measurement. At present, in the field of UHV/XHV measurement, ionization gauges based on the principle of neutral gas ionization are commonly applied to the vacuum measurement. However, traditional ionization vacuum gauges during use can create electronic excitation desorption effects, soft X-rays, and the effect of hot cathode outgassing, thereby affecting the accuracy of measurement and limiting the lower limit of measurement. Compared with the traditional measurement technology, this method uses the relationship between the loss rate and pressure caused by the collision of cold atoms trapped in the trap depth with the background gas to calculate the gas density and inversely calculate the vacuum pressure. Based on the intrinsic quantum mechanical properties of cold atom collisions, this method is expected to be developed into a new vacuum traceability standard. In this paper, based on the small-angle approximation and impulse approximation under the quantum scattering theory, the loss rate coefficient of the collision of6Li cold atoms with background gas molecules is calculated. According to the ideal gas equation, the pressure inversion formula is obtained. The collision loss rate is extracted by accurately fitting the loss curve of the cold atom. In order to improve the accuracy of vacuum inversion and reduce the influence of quantum diffractive collision on loss rate measurement, the trap depth under the conditions of a certain cooling laser intensity, detuning, and magnetic field gradient is determined by the photoassociation method. Finally, in a range of 1 × 10–8–5 × 10–6Pa, the inverted pressure value is compared with the measured value of the ionization meter, proving that this method has good accuracy and reliability in the inversion of vacuum pressure. At present, the main factor restricting the improvement of accuracy is the influence of the collision between the excited atoms in the magneto-optical trap and the background gas on the loss rate measurement. In the future, with the proportion of excited atoms and the excited stateC6coefficient to be precisely determined, the uncertainty of vacuum pressure measurement can be further reduced.
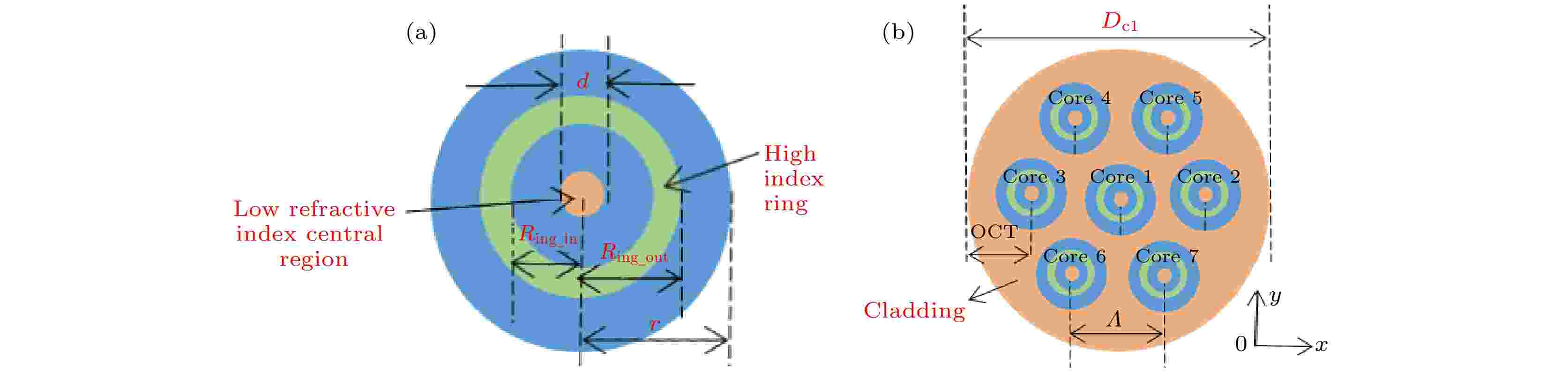
2022, 71 (9): 094205.
doi:10.7498/aps.71.20211534
Abstract +
Aiming at solving the problems of coupling between modes in a core and mode coupling between cores in few-mode multi-core fiber, a fiber with seven cores each with step index is proposed, and each core can support five modes. Each core has a central low refractive index region and a high refractive index ring to ensure that there is a large refractive index difference between modes in the core, so as to reduce the problem of mode coupling. The bending loss of central core and outer core, the crosstalk characteristics between modes and the influence of core parameters on crosstalk performance are simulated and analyzed by the finite element method. The simulation results show that at a wavelength of 1.55 μm and a bending radius of 50 mm, the bending loss of the proposed multi-core fiber is much lower than its attenuation loss, and the crosstalk between the adjacent cores of the five core modes are less than –20 dB/100 km. Therefore, this multi-core fiber can realize independent transmission of the core modes with long-distance under small bending radius.
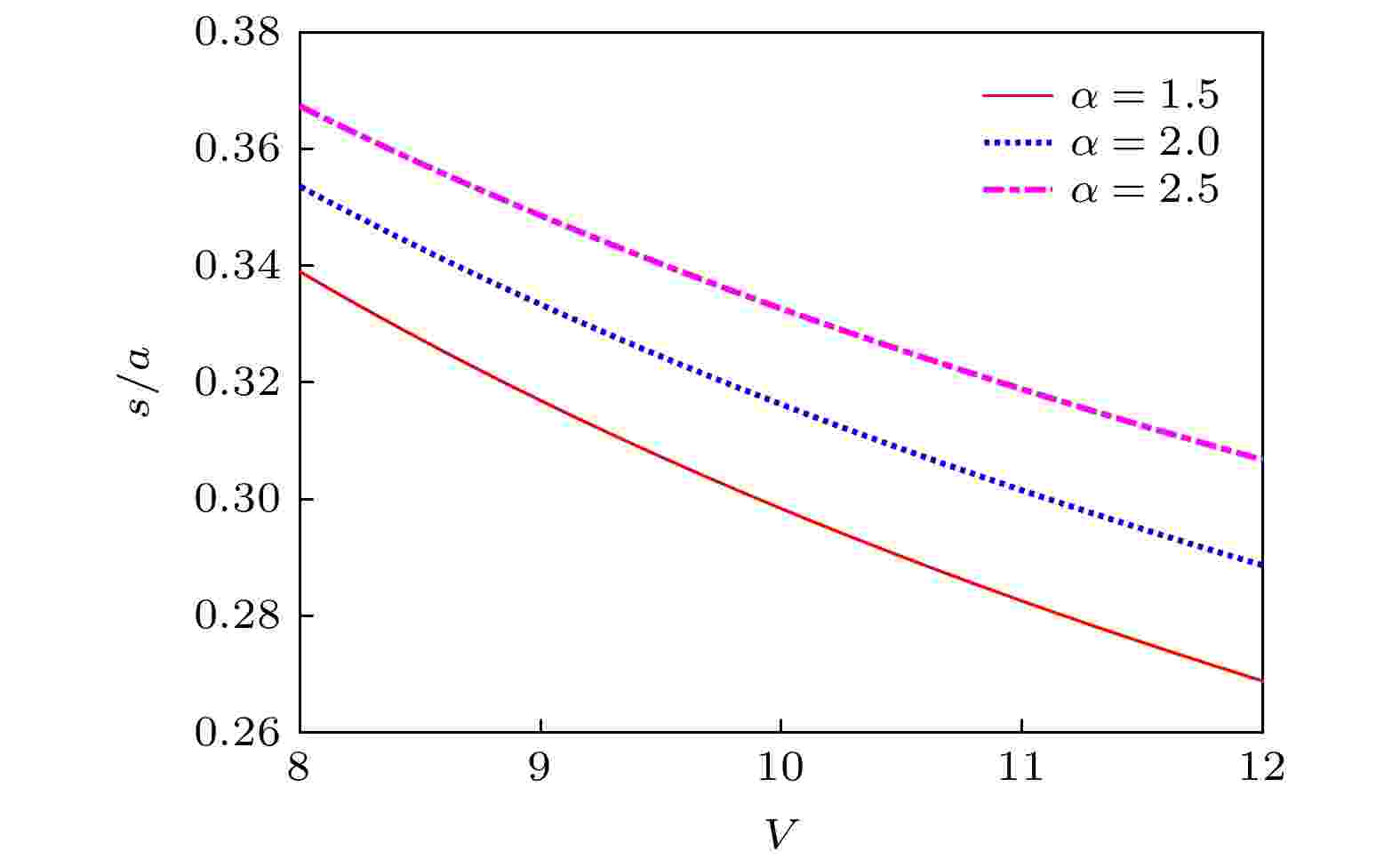
2022, 71 (9): 094206.
doi:10.7498/aps.71.20212198
Abstract +
Mode-division multiplexing (MDM) technology based on few-mode fibers (FMFs) is the current research hotspot of optical fiber communication system because of its ability to increase the transmission capacity several times. When the number of multiplexed modes is large, the crosstalk between modes can be removed by multiple input multiple output digital signal processing algorithm at the receiving end. The larger the differential mode group delay (DMGD,
$ \tau_{\rm DMGD} $
), the more complex the algorithm is. Therefore, in order to reduce the complexity of the receiver, it is necessary to use FMFs with low DMGD. The variational method is proposed to analyze any FMFs with higher refractive index of core than that of cladding. The analytical formula of the fundamental mode size, the normalized propagation constant for each of all guided modes, and DMGD relative to the fundamental mode are derived. Moreover, their relationship with the normalized frequency and other fiber manufacturing parameters are given. On this basis, the graded-index FMFs are studied, and the fiber parameters are optimized. The optimization parameters are the difference between the maximum core refractive index and cladding refractive indexn1–n2= 0.01, the core radiusa= 14 μm, and the paramenter of refractive index distributionα= 1.975. In the optimized FMF, 6 LP modes can be guided and |
$ \tau_{\rm DMGD} $
| is less than 15 ps/km within the C band and L band. In the end, the effects of the fiber manufacturing errors on DMGD are discussed.
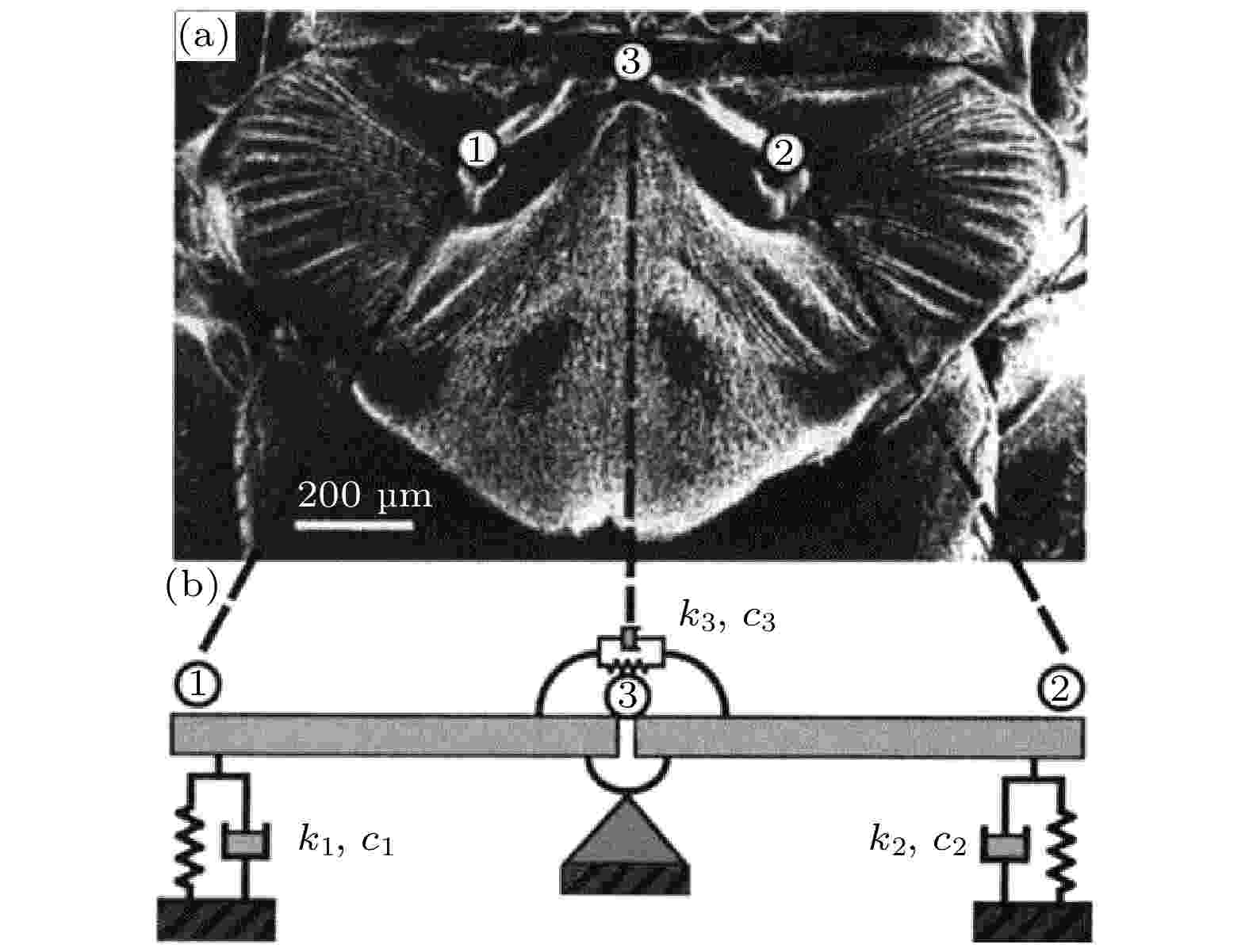
2022, 71 (9): 094301.
doi:10.7498/aps.71.20212229
Abstract +
The bionic sound detector based on the principle of the Ormia ochracea fly’s coupled ears is a miniature directional microphone that is sensitive to the sound pressure gradient. In this work, a silicon micro-electro-mechanical system bionic diaphragm consisting of two interconnected wings is designed and prepared, and a fiber-optic Fabry-Pérot interferometric microphone is constructed using the bionic diaphragm, and the characteristics of this microphone are studied theoretically and experimentally. According to the simulation results, the bionic diaphragm has two vibration modes of rocking and bending, and the rocking-mode displacement amplitude at a given sound pressure depends on the frequency and the propagation direction of the incident sound wave, and the closer to the eigenfrequency of the rocking mode the sound frequency, the greater the amplitude is; the rocking-mode displacement amplitude changes with the propagation direction in the three-dimensional space, resulting in a spindle-shaped distribution, and the long axis of the spindle is parallel to the long axis of the diaphragm, implying that the microphone is most sensitive to the sound wave propagating along the long axis of the diaphragm. The rocking-mode resonance frequency of the fiber-optic bionic microphone is measured to be slightly smaller than the simulated value. The output signal amplitude of the microphone changes with the horizontal azimuth angle of the sound source, producing a figure-8 polar pattern. A linear relationship between the microphone response and the azimuth angle is obtained in a range of 0° – ±60°, and in this angle range the directional sensitivity of the microphone is 39.98 mV/(°).

2022, 71 (9): 094701.
doi:10.7498/aps.71.20211155
Abstract +
We investigate analytically the effect of thermal conduction on the Kelvin-Helmholtz instability (KHI) in a straight pipe with different cross-sections. The results show that the relative tangential velocity of the interface between the upper and lower fluid in the pipe first increases and then decreases with the increase of the wave number. Furthermore, the smaller coefficient of interfacial heat conduction causes the relative tangential velocity to decrease considerably with the increase of the wave number, which is different from the behavior of the straight pipeline with the same cross-section. In addition, the heat conduction increases the growth rate of KHI, which is in accordance with the scenario of straight pipeline with the same cross-section.
PHYSICS OF GASES, PLASMAS, AND ELECTRIC DISCHARGES
EDITOR'S SUGGESTION
2022, 71 (9): 095201.
doi:10.7498/aps.71.20212136
Abstract +
Laser-driven flyer has been studied for decades as it promises to possess many applications such as in measuring the equation of state (EOS) under ultrahigh pressure, investigating the material dynamic properties under high strain rate, simulating the high-speed impact for aircraft protection, and igniting explosives. However, the planarity and integrity of flyers are determined by indirect velocity lnterferometer system for any reflector (VISAR) or witness slab results due to its high speed and small dimension. For further and wide applications, it is very important to obtain direct experimental proof of the flyer gesture and configuration. Thus, the acceleration and gesture investigation of aluminum flyer driven by laser plasma are studied on Xingguang-III laser facility. The X-ray radiography is achieved by a picosecond laser irradiating the copper wire target. The shadowgraph of flyer and plasma are realized by the incidence of a bunch of infrared laser through the flyer flight path. In additon, photon Doppler velocimetry is employed to measure the flyer velocity simultaneously. The radiography, shadowgraph and velocity of typical small aluminum flyer are obtained. By optimizing the thickness of both CH ablation layer and vacuum gap, the flyer is slowly accelerated via consecutive stress wave produced by plasma colliding. The aluminum flyer has a thickness of 20 μm and diameter of about 500 μm. The whole flyer remains the integrated shape after a great angle of rotation due to uneven plasma loading. The flight distance is about 400 μm, giving an average velocity of 2.2 km/s. The planarity of the flyer is good except a little bend on the two sides due to side rarefaction of plasma. The study verifies that the laser plasma collision can generate a sub-millimeter-diameter metal flyer with integrated shape and a velocity of several kilo-meters per second, showing that it possesses the promising applications in measuring the EOS and igniting explosive .
COVER ARTICLE
2022, 71 (9): 095202.
doi:10.7498/aps.71.20212435
Abstract +
Preformed plasma channels play important roles in many applications, such as laser wakefield acceleration, plasma lens, and so on. Laser pulses can be well guided when the radial density distribution of the plasma channel has a parabolic profile and it is matched with the laser focus. Discharging a gas-filled capillary is a possible way to form such plasma channels. In this work, we report the capillary discharging and laser guiding experiments performed in the Laboratory for Laser Plasmas at Shanghai Jiao Tong University. The plasma density distributions in the Helium-filled discharged capillary are measured by using the spectral broadening method. In a capillary with a length of 3 cm and a diameter of 300 μm, the plasma density profile is observed to be uniformly distributed along the axial direction and have a parabolic profile along the radial direction. Parameters for plasma channel generation are scanned. The deepest channel depth obtained is 28 μm, which is close to the focal spot radius of the laser used in the experiment. Laser guidance in the plasma channel is also studied. The results show that the laser can maintain its focus and continuously propagate when the channel depth matches the focal spot, indicating that the well guiding of the laser pulse by the preformed plasma channel is obtained. These studies may serve as the ground work for the future studies, such as staged laser wakefield acceleration and phase-locked wakefield acceleration.
2022, 71 (9): 095203.
doi:10.7498/aps.71.20210902
Abstract +
The propagation characteristics of (2 + 1) dimensional nonlinear dust acoustic solitary wave in an unmagnetized hot dusty plasma composed of dust particles, electrons and nonthermal ions are studied in the paper. Firstly, the Kadomtsev-Petviashvili (KP) equation, which is used to describe the (2 + 1) dimensional nonlinear dust acoustic solitary wave, is derived by the reduced perturbation method, and the phase diagram and the Sagdeev potential equation of the system are obtained by using the traveling wave solution method. Then, the effects of different parameters in the hot dusty plasma system on the nonlinear coefficient, dispersion coefficient of the KP equation, system phase diagrams, Sagdeev potential function and the solitary wave solution in isothermal and adiabatic states are discussed by using numerical simulation and analysis method of mathematical software. Finally, the results show that the mass of dust particles, temperature, number density and distribution state of electrons and nonthermal ions have important effects on the amplitude, width and waveform of the nonlinear dust acoustic solitary wave under isothermal and adiabatic conditions.
CONDENSED MATTER: STRUCTURAL, MECHANICAL, AND THERMAL PROPERTIES
2022, 71 (9): 096101.
doi:10.7498/aps.71.20212276
Abstract +
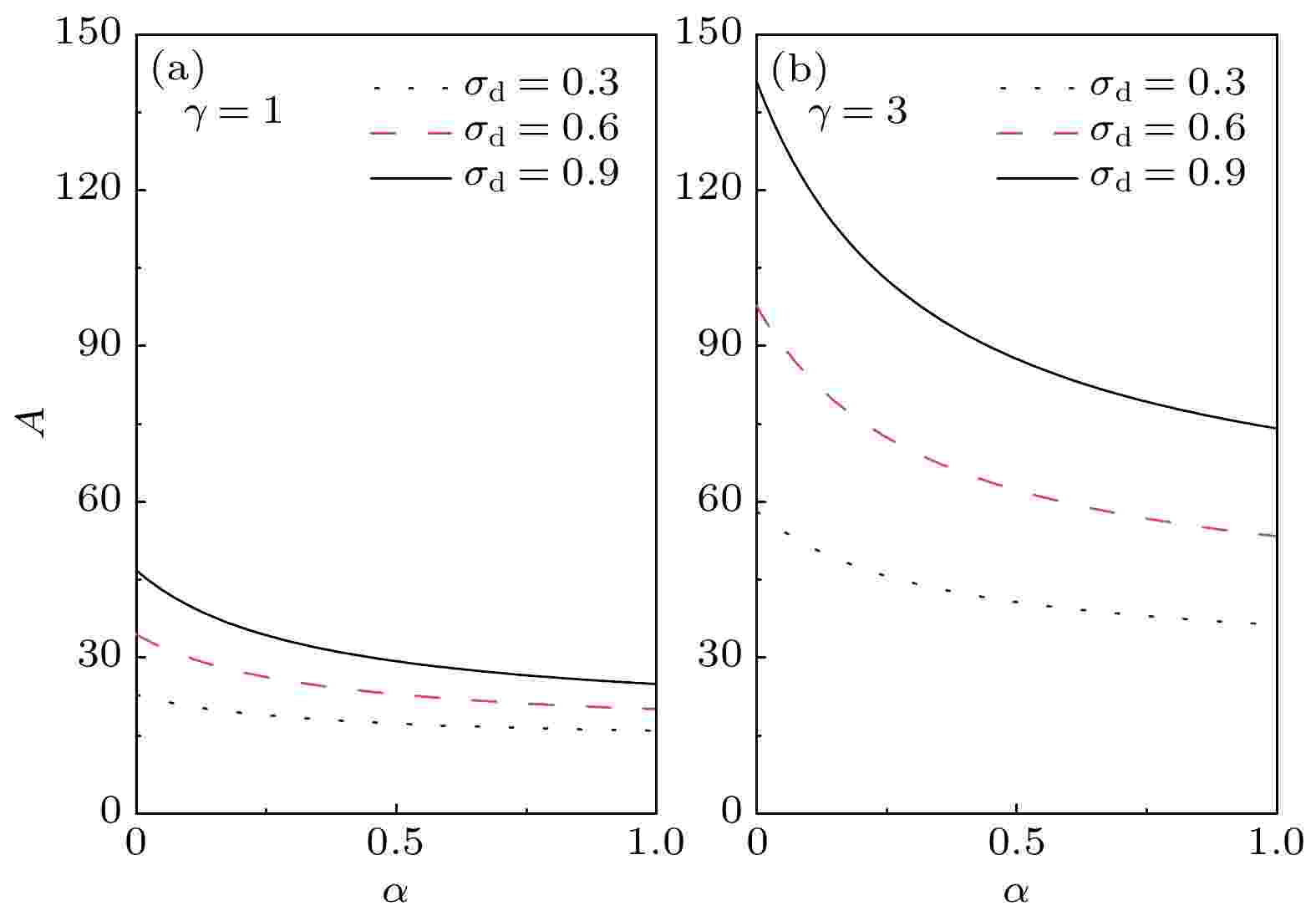
In this work, anatase Titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanowires are synthesized by the hydrothermal method, and its grain and grain boundary behaviors and electrical properties are investigated by alternating current (AC) impedance method under high pressure (up to 34.0 GPa). The relationship between the frequency dependence of impedanceZ''and pressure indicate that the conduction mechanism of anatase phase TiO2nanowires in the test pressure range is electronic conductivity. It should be noted that the characteristic peaks ofZ''move toward high frequency region with pressure increasing, demonstrating that the effect of grain interior on impedance becomes apparent. Additionally, the overall variation trends of grain and grain boundary resistance go downward with pressure increasing, and the descent rate of grain boundary is larger than those of grain before and after phase transition. However, in a range of phase transition (8.2–11.2 GPa, from anatase to baddeleyite phase), grain boundary resistance shows a discontinuously change (increases to 11.2 GPa and then decreases). Based on the different variation trends of grain and grain boundary resistance, it becomes obvious that the phase transition from anatase to baddeleyite phase first occurs at the surface of grain, and then extends to the interior of grain gradually. Also, as an intrinsic characteristic, the relaxation frequency is independent of the geometrical parameters. The pressure dependence of activation energy is obtained by fitting the pressure dependence of relaxation frequency. The activation energy of grain and grain boundary decrease with pressure increasing, implying that the contribution of pressure on the conductivity of sample is positive. Furthermore, the space charge potential for the whole test pressure range is positive, which is determined by the relationship between pressure and relaxation frequency. This fact illustrates that the anion defects are easily formed in the space charge region, and the oxygen defects are the main inducement for TiO2phase transformation.
2022, 71 (9): 096102.
doi:10.7498/aps.71.20212278
Abstract +
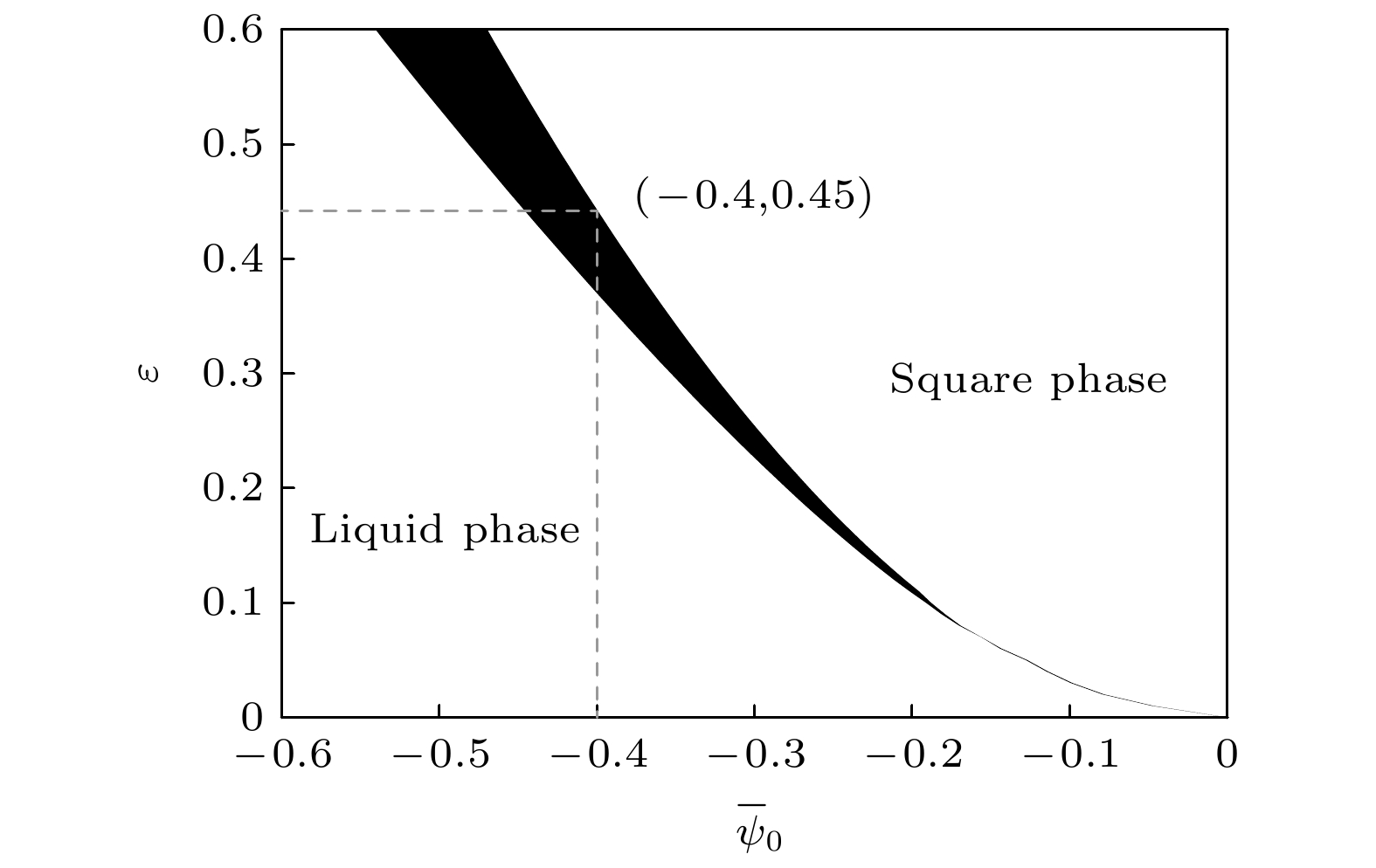
In this paper, the phase field crystal method is used to study the dislocation motion and reaction of the square phase symmetric tilt low-angle grain boundaries, and the dislocation configurations with different misorientation angles are analyzed under the action of applied strain. The geometric phase approach is used to characterize the strain field around the dislocations. The results show that after the solidification relaxation, the interfacial dislocations on both sides of the grain are distributed in parallel but opposite direction. With the increase of misorientation angle between grains, the number of dislocations increases, the spacing between them decreases, and the free energy of the system increases. Imposed by the applied strain, the grain boundary dislocations undergo climbing, launching, and reactive annihilation, with the free energy fluctuating. When the misorientation increases, the dislocation motion mode changes from climbing to climbing-sliping, resulting in more dislocation group configurations, and more reactions between dislocations and dislocation groups. For the dislocation reactions of different configurations, positive shear strain drives dislocations to approach, and negative shear strain drives dislocations to annihilate.
EDITOR'S SUGGESTION
2022, 71 (9): 096103.
doi:10.7498/aps.71.20212316
Abstract +
In recent decades, as a kind of critical material in spintronics field, the diluted magnetic semiconductor with high temperature and intrinsic ferromagnetism has attracted extensive attention. In order to explore the approach to enhancing Curie temperature (TC), the LDA+Umethod of the first-principles calculation is adopted to study the effect of strain on electronic structure, magnetic and optical properties in Mo doped GaSb system. The results indicate that the structure of GaSb is stable with strain in a range of –6%—2.5%. Plasticity and toughness of GaSb increase under compressive strains, which is conducive to the improvement of the mechanical properties. The strain affects the electronic structure of MoGagreatly. In a range from –3% to –1.2%, MoGais in the low spin state (LSS) with a 1
${\mu _{{\rm{B}}}}$
local magnetic moment, while in a range of –1.1%—2%, MoGais in high spin state (HSS) with a 3
${\mu _{{\rm{B}}}}$
moment. The magnetic interactions between MoGaand MoGaare all ferromagnetic for LSS and so is the case for HSS, although they are different in coupling intensity and mechanism. In particular, appropriate compressive strains can improve the strength of ferromagnetic coupling effectively and are favorable for the preparation of the GaSb-based diluted magnetic semiconductors with high Curie temperatures and inherent ferromagnetism. Moreover, we find that Mo can greatly improve the polarization capability of GaSb and play a vital role in forming and separating the electron-hole pairs, and thus further improving the photoelectric conversion capability for long wave photons. The energy required to absorb photons for inter-band transition of electrons decreases because of the impurity levels induced by Mo, which leads the absorption edge to be red-shifted. The optical properties of (Ga,Mo)Sb in infrared region are further enhanced by the tensile strain.
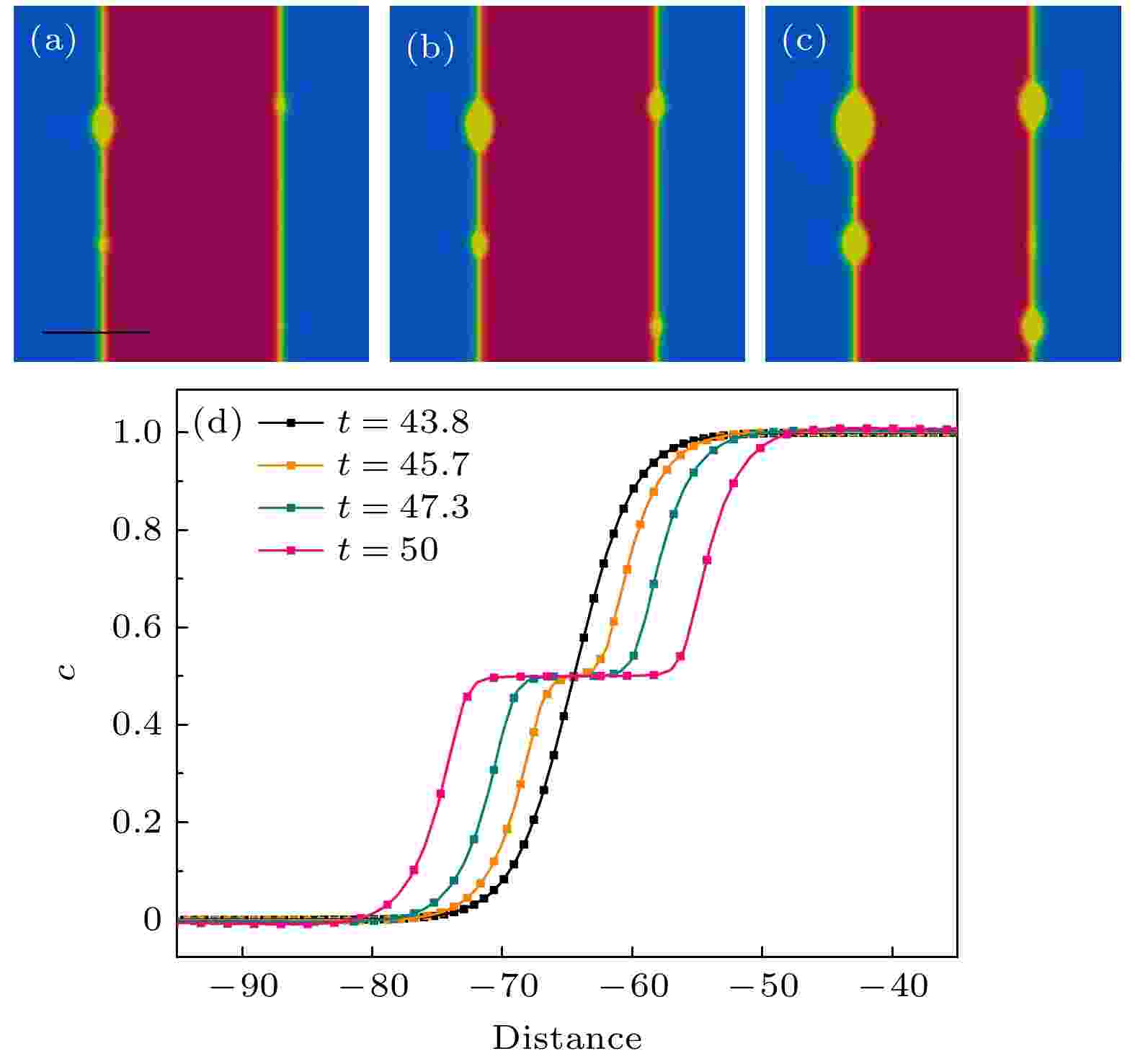
2022, 71 (9): 096401.
doi:10.7498/aps.71.20211737
Abstract +
Thein-situreaction is an important method of preparing metal matrix composites: it can produce more uniform distribution of the reinforcement particles and more excellent structure of the phase boundary between the particles and the matrix. Therefore, the kinetics ofin-situreaction process deserves to be further studied. However, as thein-situreaction is a rapid random process under high-temperature condition, it is difficult to observe the reaction process of metal-matrix composite materials experimentally. In this work, we propose a new phase-field model to describe thein-situreaction process, and investigate the nucleation kinetic processes ofin-situreaction under different physical conditions. We find that the nucleation rate increases with the augment of curvature radius and noise intensity, and the size distribution of the particles is more uniform under the conditions of a small curvature radius and strong noise. With the increase of the undercooling, the nucleation rate first increases and then decreases, which is consistent with the classical nucleation theory.
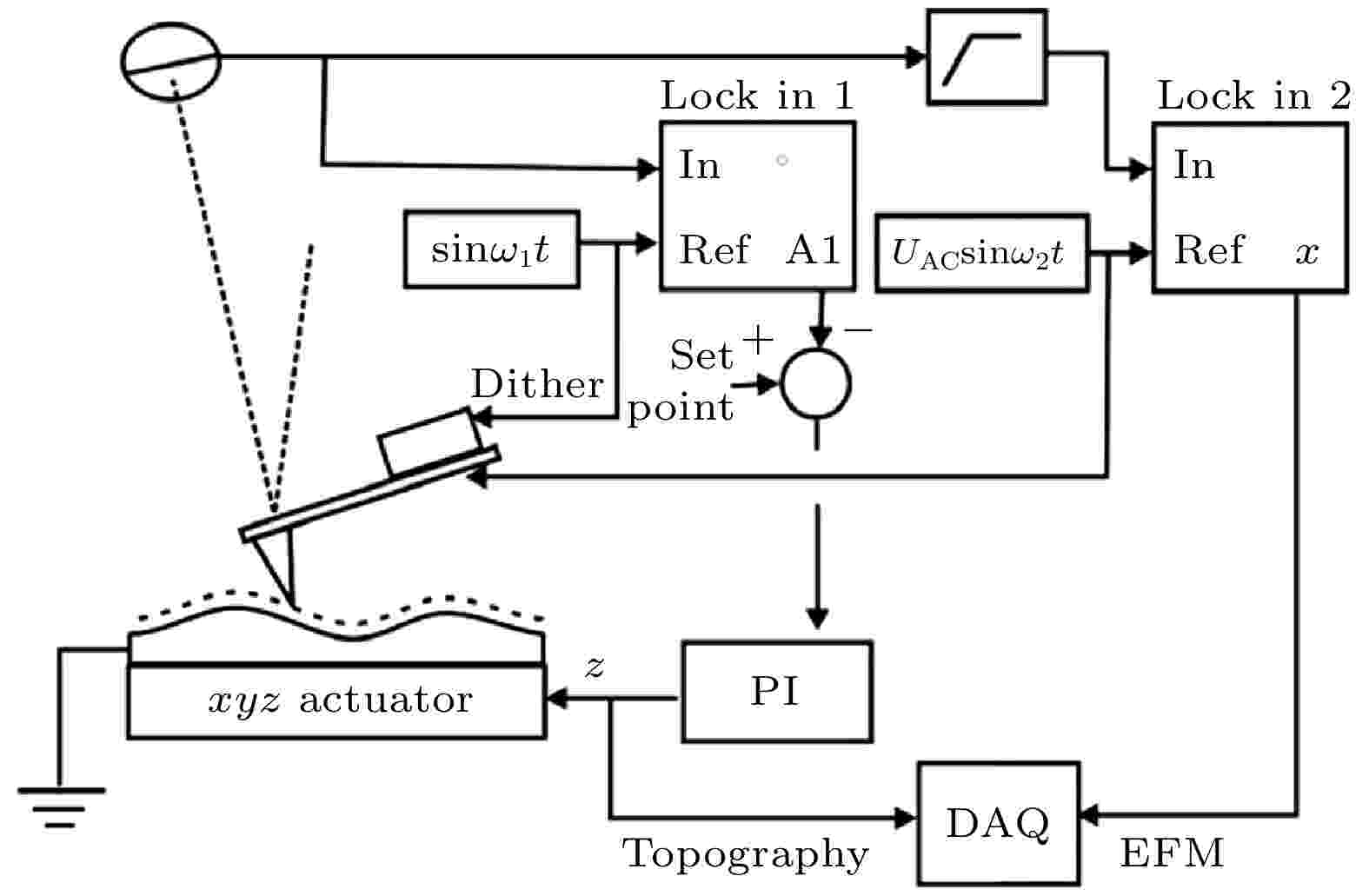
2022, 71 (9): 096801.
doi:10.7498/aps.71.20212095
Abstract +
Electrostatic force microscopy (EFM) has high sensitivity and lateral resolution, and it is widely used to measure the electrostatic properties of new energy materials. The time-resolved electrostatic force microscope technology is used to measure the dynamic electrical properties of materials, pump detection method commonly used in this technology has problems such as complex equipment, high cost, and uncertainty in the measurement. In this work the method of directly measuring the time domain is adopted. This method reduces the complexity of measurement. By using the multi-frequency or high-frequency excitation method, the simultaneous measurement of multiple EFM parameters and the improvement of time resolution can be achieved, reaching a time resolution of microseconds, and by applying wavelet transform to the tip signal obtained by the measurement the dynamic electrical properties of the materials can be extracted. Applying this technology to simulation experiments, it is possible to measure the dynamic potential changes and the characteristic time parameter of ion movement in the microsecond-level electrical dynamic process of the simulated battery materials.
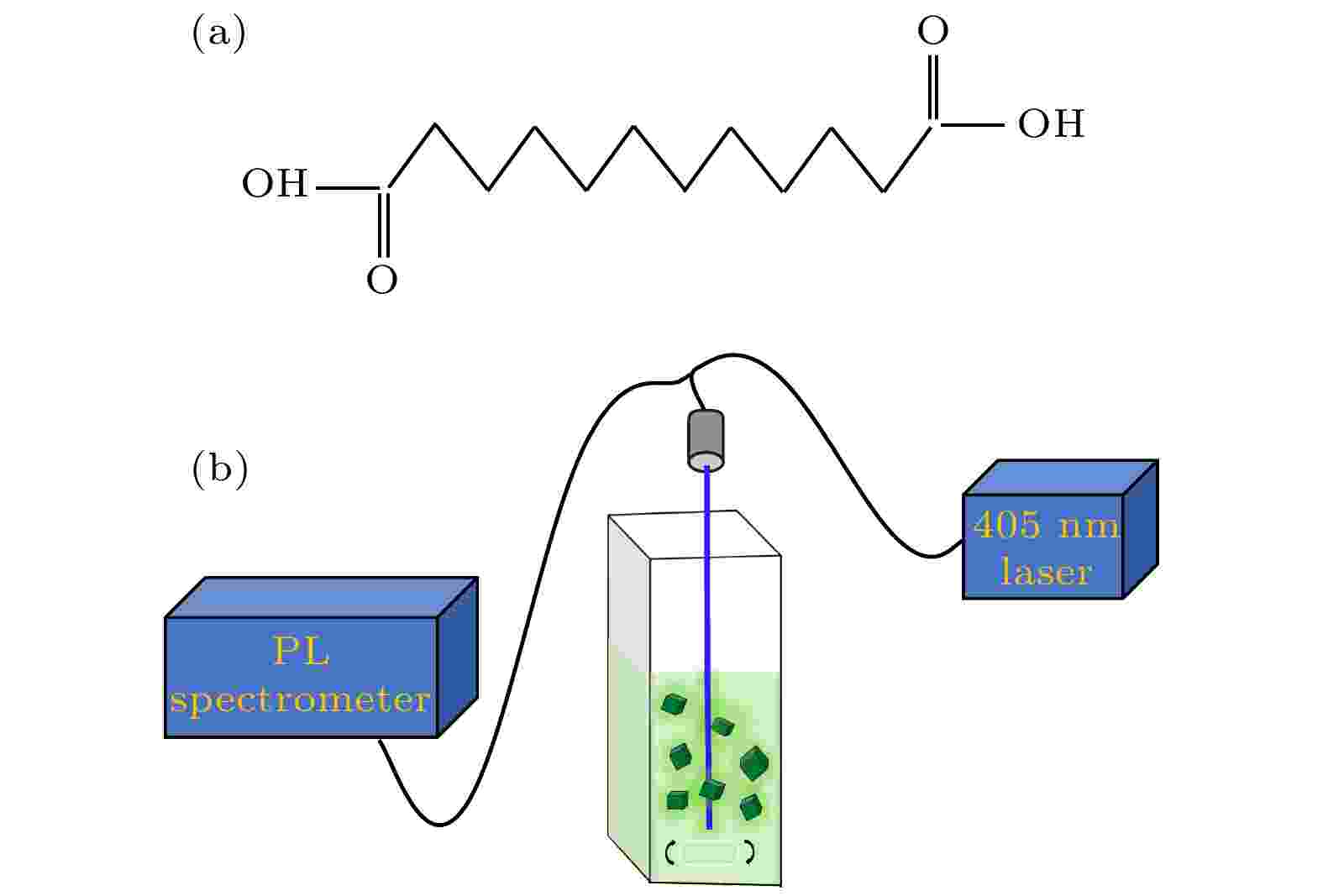
2022, 71 (9): 096802.
doi:10.7498/aps.71.20212228
Abstract +
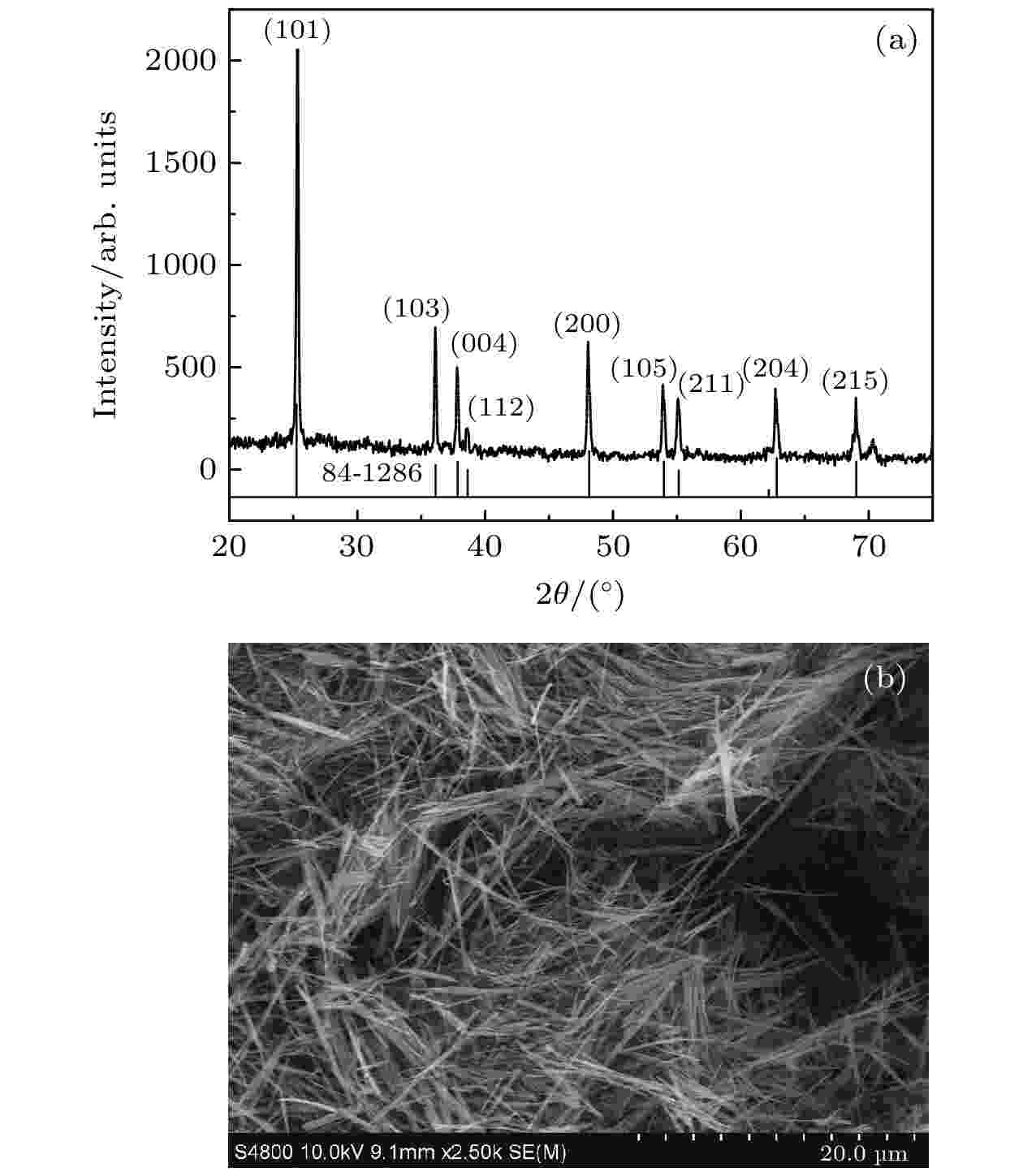
Cesium-lead halide perovskite nanocrystals (CsPbX3(X= Br, Cl, I) PNCs) have become ideal luminescent materials for wide color gamut display devices, white LED lighting and high-efficiency solar cells, due to adjustable energy band gap, high fluorescence quantum yield, narrow fluorescence emission peak, and ultra-high defect tolerance. The preparation of CsPbX3PNCs with controllable size and morphology is a prerequisite for obtaining efficient and stable photovoltaic/photovoltaic devices. In this report, the CsPbBr3PNCs with different shapes are prepared by adding different concentrations of dodecanedioic acid (DDDA) ligands at room temperature through using ligand-assisted reprecipitation method. Utilizing the X-ray diffractometer, transmission electron microscopy, ultraviolet spectrophotometer, fluorescence spectrometers (PL), the phase structure, microstructure and optical properties of the nanocrystals are investigated. The results show that the presence of DDDA ligands have no influence on the phase structure of nanocrystal products, they all present a cubic phase structure. Surprisingly, the morphology of the nanocrystals gradually transforms from nanocubes into nanoplatelets with ~5 layers in thickness as the concentration of DDDA increases. In addition, the PL spectrum shows a significant blue shift from 509 nm to 478 nm. By using thein-situhomemade PL device with ultra-high time resolution (~100 ms), the real-time monitoring PL spectra of nanocrystals in the formation process are measured. The results demonstrate that nanocrystals undergo rapid nucleation and focusing of size distribution growth to generate nanocubes in the absence of DDDA ligand. When the DDDA ligand is present, nanocrystals are mainly nanoplatelets in the early growth stage due to the decelerated reaction. As the reaction proceeds, nanocubes can emerge and grow gradually while the nanoplatelets disappear when the concentrations of DDDA ligands are 25% and 50%. As the concentration is further increased to 75%, almost nanoplatelets could be formed after the nucleation stage and growth stage. Unexpectedly, preformed nanoplatelets are unstable for the prolonged reaction time as a result of the high surface energy, and they will eventually transform into isotropic nanocubes through dissolution-recrystallization pathway, indicating that the process in the later stage is controlled mainly by thermodynamics. Our findings offer an efficient strategy to synthesize the perovskite nanocrystals with controllable size and morphology.
CONDENSED MATTER: ELECTRONIC STRUCTURE, ELECTRICAL, MAGNETIC, AND OPTICAL PROPERTIES
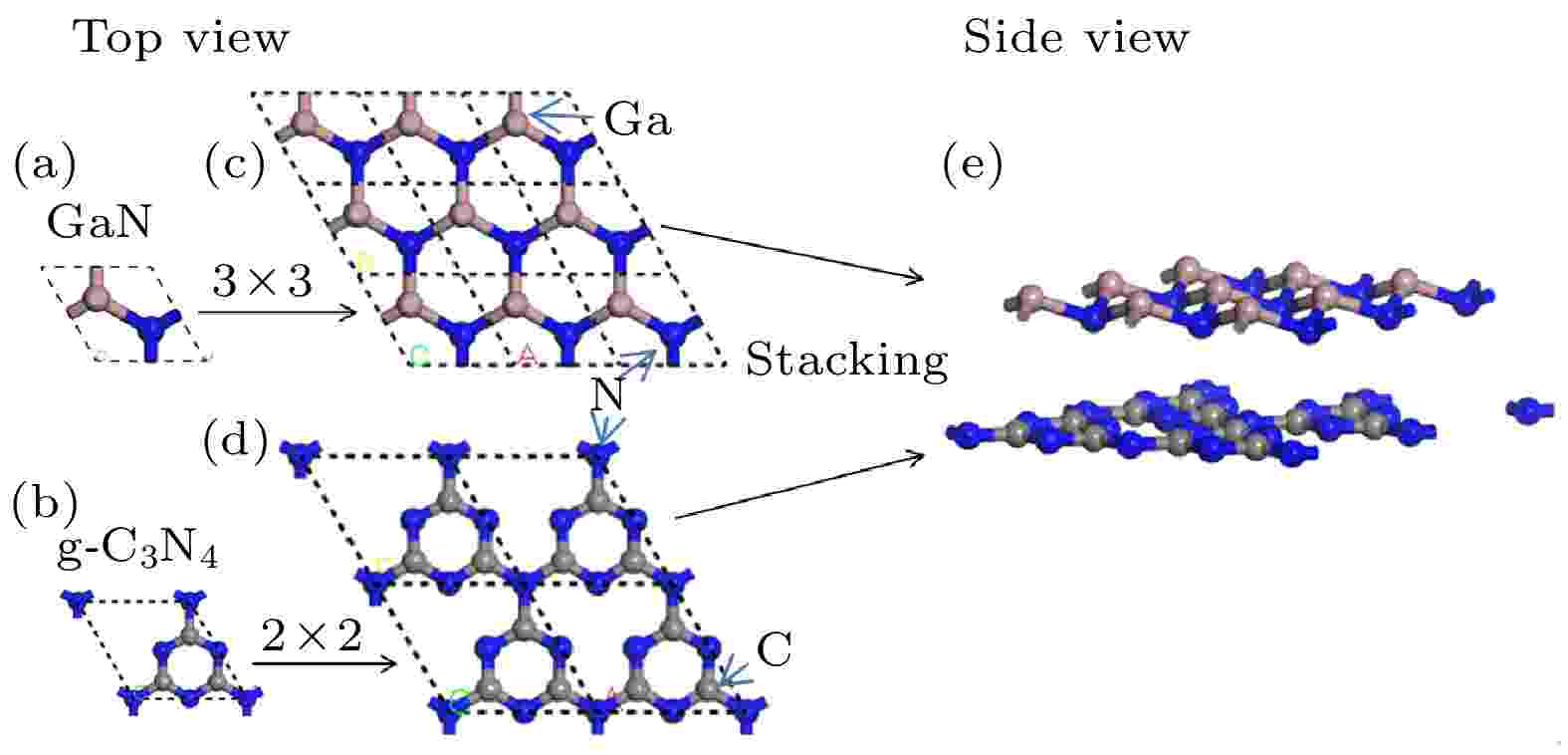
2022, 71 (9): 097301.
doi:10.7498/aps.71.20212261
Abstract +
In this paper, the stability, electronic structure, optical properties, and work function of GaN/g-C3N4heterojunction are studied by using the first-principles plane wave ultra-soft pseudopotential method based on density functional theory. The electric field effect is also considered. The results show that the total energy for each of the three stacking modes changes little for using the two different dispersion correction methods, i.e. Tkatchenko-Scheffler and Grimme, and the total energy of mode II is the lowest, indicating that the structure of mode II is the most stable. The lattice mismatch ratio and lattice mismatch energy of GaN/g-C3N4van der Waals heterojunction are very low, indicating that the heterojunction has good stability. The heterojunction retains the basic electronic properties of GaN and g-C3N4to a great extent and can be used as a direct bandgap semiconductor material. It can be known from the work function and differential charge diagram that the charge on the heterojunction interface is transferred from GaN to g-C3N4, and a built-in electric field orientating g-C3N4from GaN is formed at the interface. The built-in electric field of the heterojunction can effectively separate the photogenerated electron-hole pairs, which is conducive to improving the photocatalytic capability of the system. Further analysis shows that the applied electric field reduces the bandgap of GaN/g-C3N4heterostructure to varying degrees. It makes it easier for electrons to transit from valence band to conduction band, which is conducive to improving the photocatalytic activity of the system. In addition, when the applied electric field is –0.6 V/Å and 0.5 V/Å separately, the semiconductor metal phase transition occurs in the heterojunction. When the applied electric field is higher than 0.3 V/Å and lower than –0.4 V/Å, in the energy band arrangement of the heterojunction there occurs the transition from type I to type II. This can better realize the separation of photogenerated electron-hole pairs and further improve the photocatalytic capactivity of the system. Therefore, the construction of heterojunction and application of external electric field proposed in this work constitute an effective means to improve the photocatalytic activity of the system.
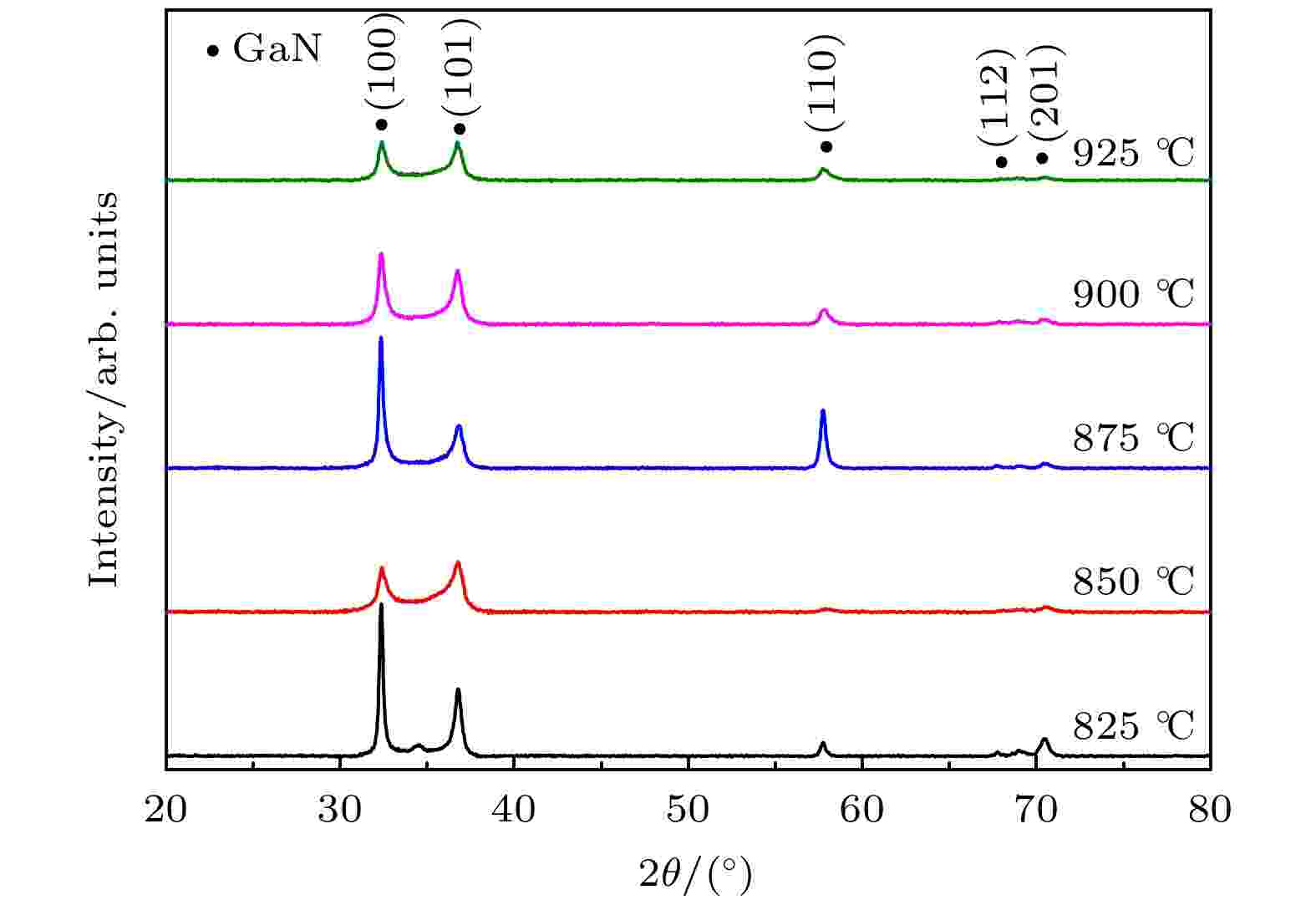
2022, 71 (9): 097302.
doi:10.7498/aps.71.20211922
Abstract +
In this study, the high-quality GaN films are prepared by a simple, green and low-cost plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) method at 950 ℃, with Ga2O3and N2serving as a gallium source and a nitrogen source, respectively. In order to improve the crystal quality of GaN films and ascertain the photoresponse mechanism of GaN films, the effect of the preparation temperature of GaN buffer layer on the crystal quality and photoelectric properties of GaN thin films are investigated. It is indicated that with the increase of the buffer temperature of GaN films, the crystal quality of GaN films first increases and then decreases, and the highest crystal quality is obtained at 875 ℃. When buffer layer temperature is 875 ℃, the calculated total dislocation density is 9.74 × 109cm–2, and the carrier mobility is 0.713 cm2·V–1·s–1. The crystal quality of GaN film after being annealed is improved. The total dislocation density of GaN film decreases to 7.38 × 109cm–2, and the carrier mobility increases to 43.5 cm2·V–1·s–1. The UV-Vis absorption spectrum results indicate that the optical band gap of GaN film is 3.35 eV. The scanning electron microscope (SEM) results indicate that GaN film (buffer layer temperature is 875 ℃) has smooth surface and compact structure. The Hall and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) results indicate that there are N vacancies, Ga vacancies or O doping in the GaN film, which act as deep level to capture photogenerated electrons and holes. With the bias increasing, the photoresponsivity of the GaN film photodetector gradually increases and then reaches a saturation value. This is due to the deep levels produced by vacancy or O doping. In addition, photocurrent response and recovery of GaN film are slow, which is also due to the deep levels formed by vacancy or O doping. At 5-V bias, the photoresponsivity of GaN film is 0.2 A/W, rise time is 15.4 s, and fall time is 24 s. Therefore, the high-quality GaN film prepared by the proposed green and low-cost PECVD method present a strong potential application in ultraviolet photodetector. The PECVD method developed by us provides a feasible way of preparing high-quality GaN films, and the understanding of the photoresponse mechanism of GaN films provides a theoretical basis for the wide application of GaN films.
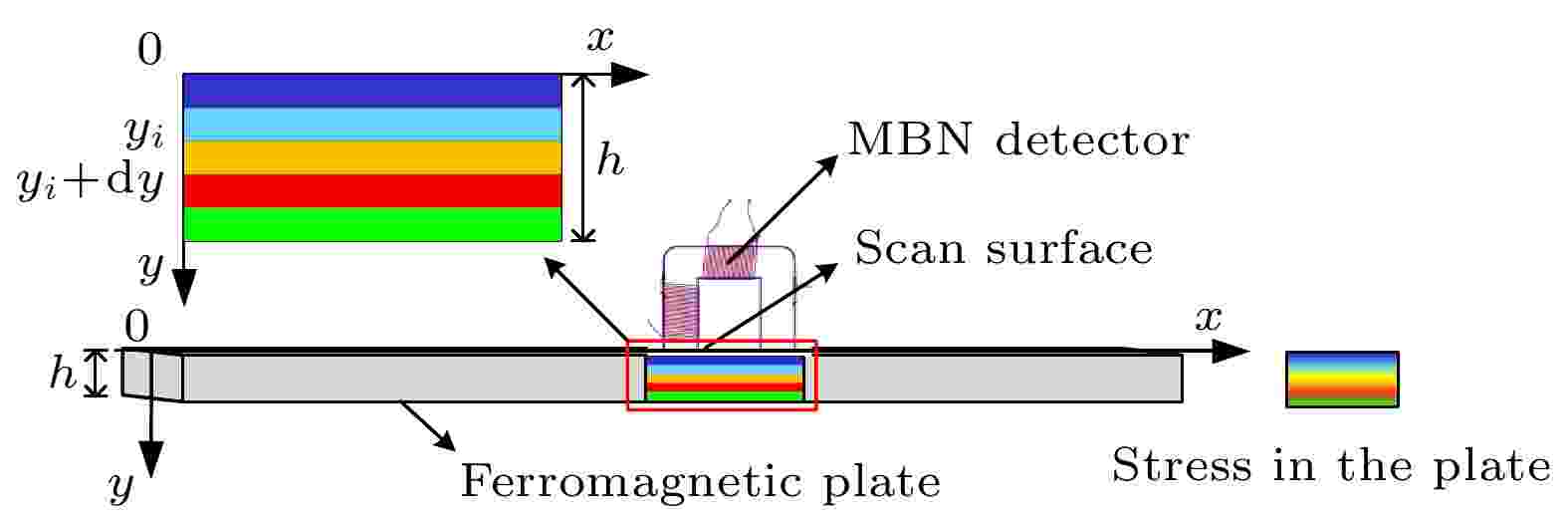
2022, 71 (9): 097501.
doi:10.7498/aps.71.20212253
Abstract +
As one of the important non-destructive testing techniques for evaluating material performance degradation and stress state, magnetic Barkhausen noise (MBN) has broad application prospects. Clarifying the relationship between internal stress distribution and detection signal can provide important guidance for evaluating the stress state of material based on the MBN signal. In this work, by constructing the expression of Barkhausen noise excitation intensity related to stress value, combining with the signal attenuation effect during signal propagation, and using the layered model along the thickness direction, we establish the analytical model of MBN signal on the surface of the ferromagnetic plate with internal stress distribution. Based on the existing experimental results, it is confirmed that the proposed model can reflect the effects of the different uniform stresses in the ferromagnetic plate on the signal at different detection frequencies. For the ferromagnetic plate with internal stress distribution, the effects of its stress distribution, magnetic conductivity, electrical resistivity, and thickness on the surface MBN signal are discussed in detail based on the proposed model. The theoretical analysis in this work can be applied to the testing mechanism analysis of the MBN stress evaluation method.
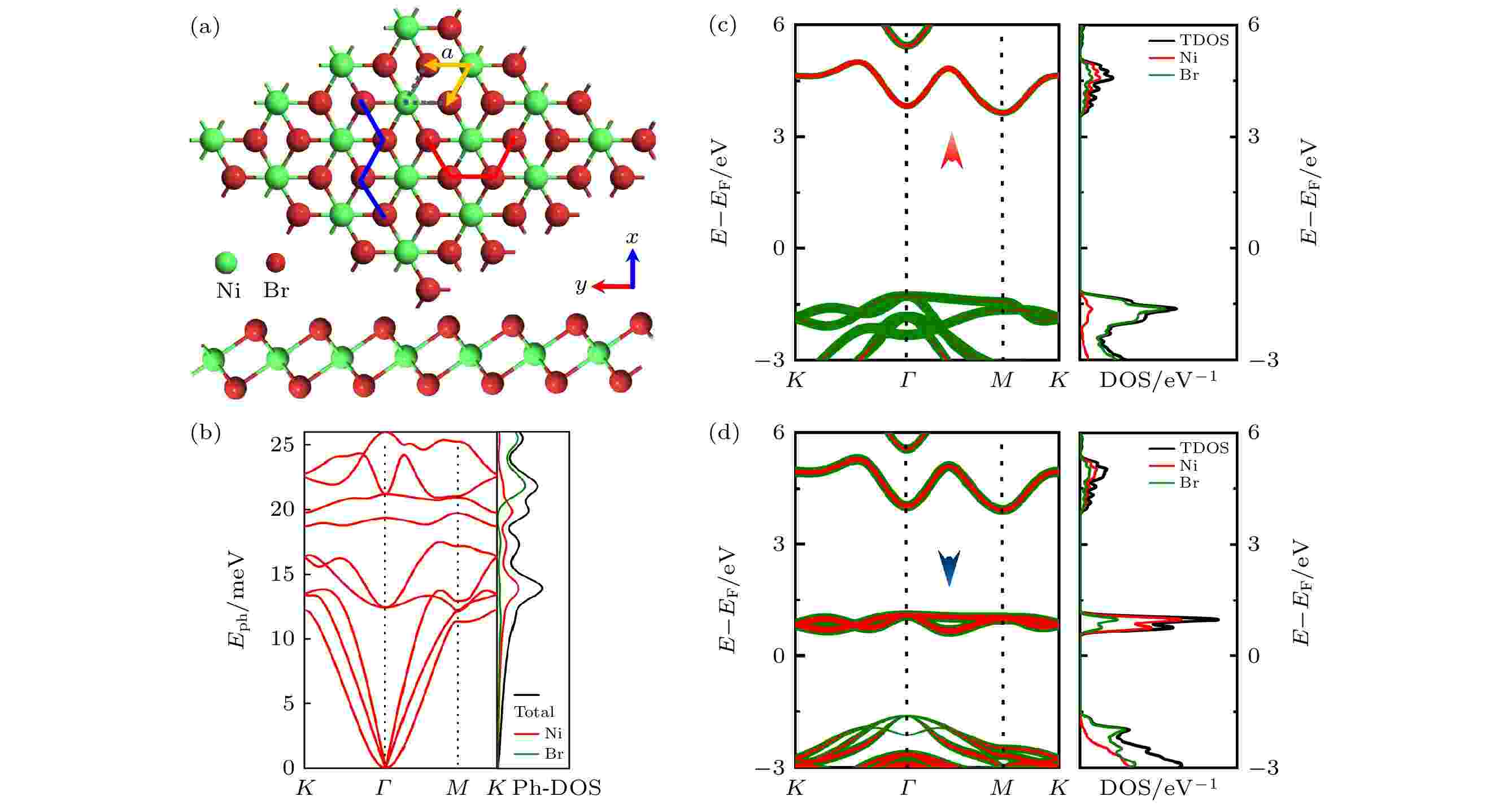
EDITOR'S SUGGESTION
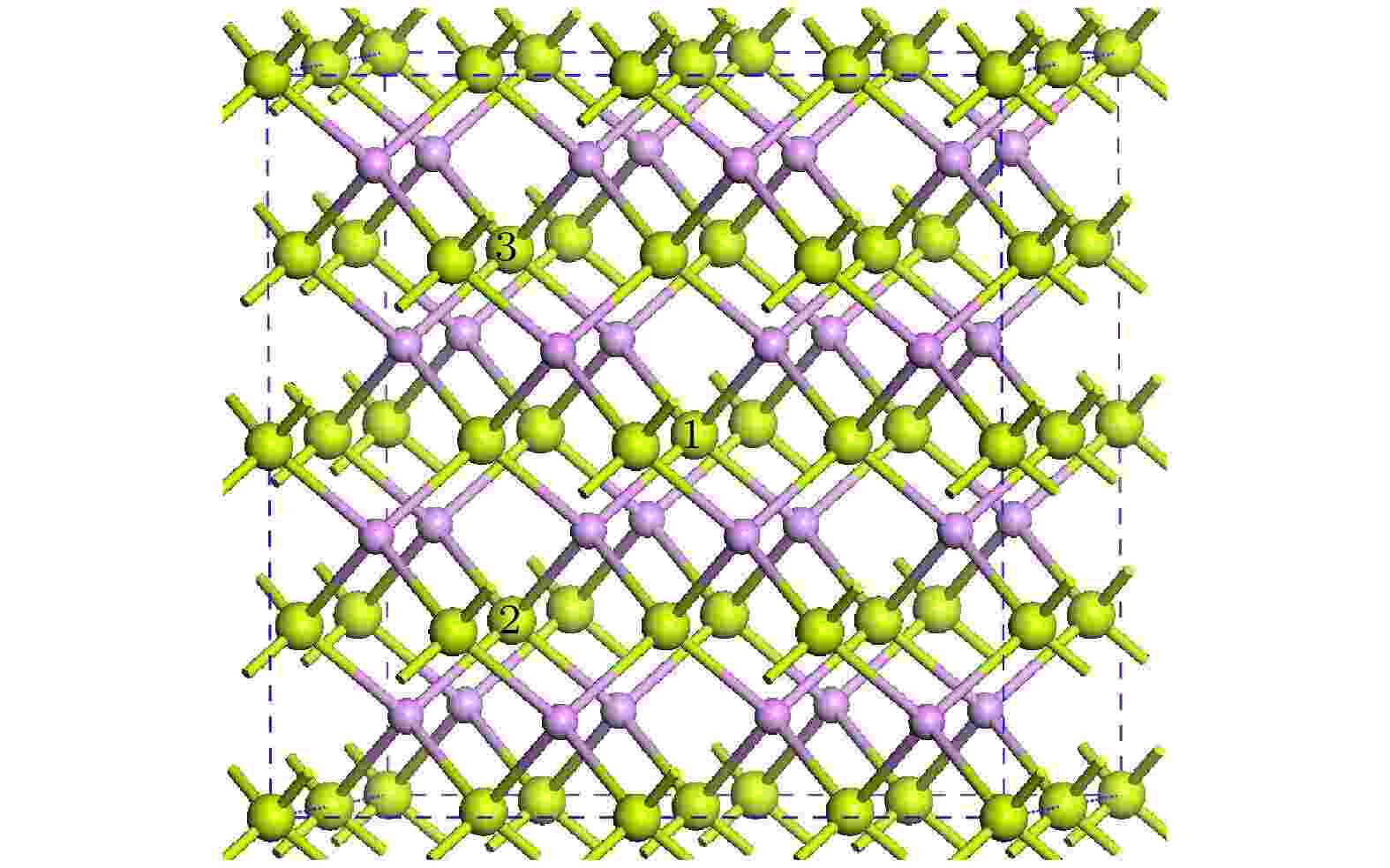
Spin transport characteristics and photoelectric properties of magnetic semiconductor NiBr2monolayer
2022, 71 (9): 097502.
doi:10.7498/aps.71.20212384
Abstract +
Magnetic semiconductor materials have potential applications in spintronic devices. In this work, some nano-device structures based on the magnetic semiconductor NiBr2monolayer (NiBr2-ML) are designed, their spin-resolved transport and photoelectric properties are studied by using density functional theory combined with non-equilibrium Green’s function method. The results show that both the NiBr2-ML PN-junction diodes and sub-3 nanometer PIN-junction field-effect transistors (FETs) exhibit the significant rectification and spin filtering effects in either the armchair or the zigzag direction. The gates can obviously tune the electron transmission of the PIN-junction FETs. The current is significantly suppressed with the increase of gate voltage. In addition, NiBr2-ML has a strong response to the blue and green light, thus its phototransistor can generate a strong photocurrent under the irradiation of blue and green light. The research results in this paper reveal the multifunctional characteristics of NiBr2-ML, which provides an important reference for the application of nickel-based dihalides in semiconductor spintronic devices and optoelectronic devices.
EDITOR'S SUGGESTION
2022, 71 (9): 097701.
doi:10.7498/aps.71.20220234
Abstract +
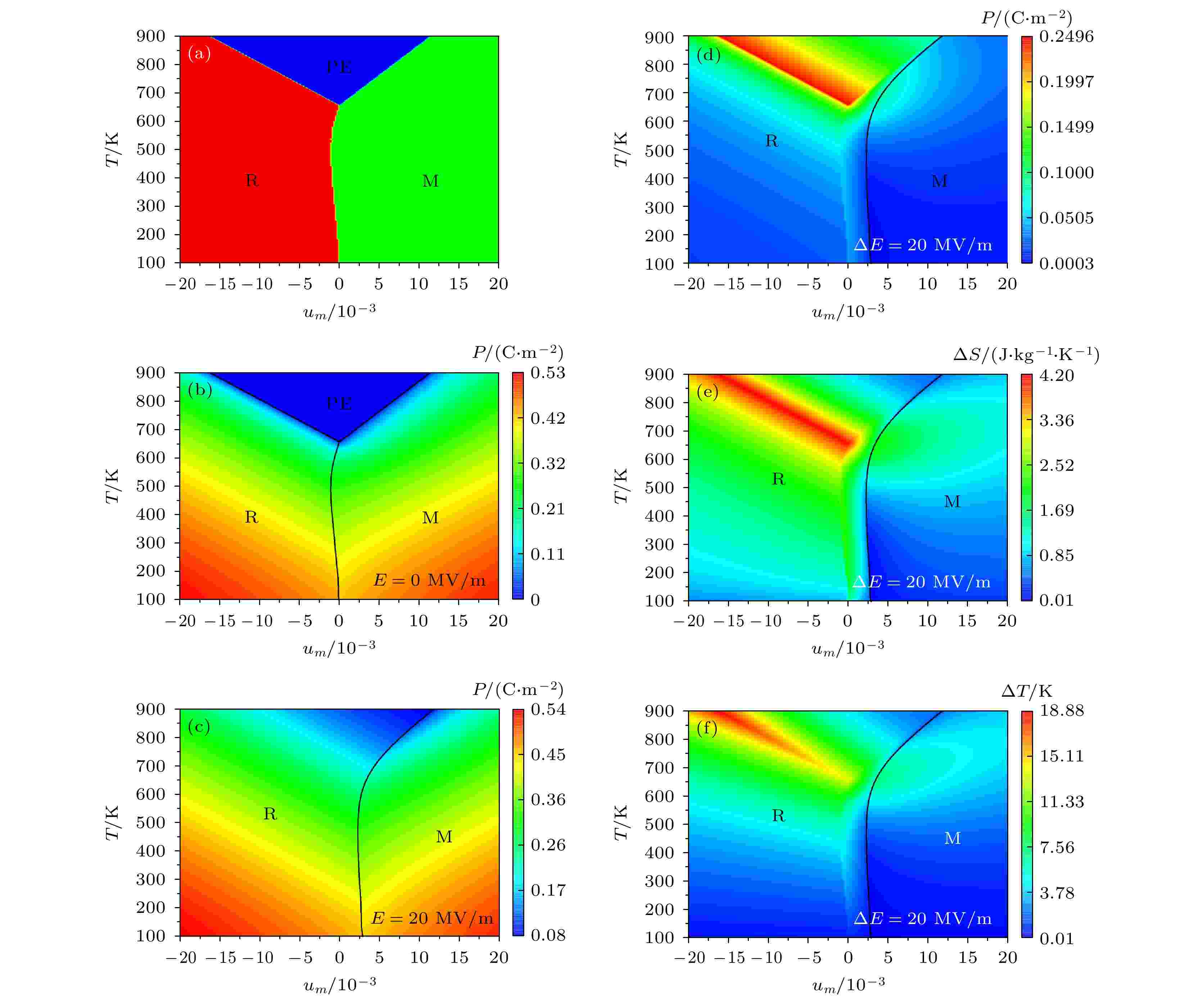
Lead-free K1–xNaxNbO3thin films, as a candidate for sensors and electromechanical and electrocaloric cooling devices, have increasingly received attention. However, for (111)-oriented films, the relation between phase transitions and electrocaloric effect is not clear. Here, we derive the thermodynamic potential of (111)-oriented thin film ferroelectrics K1–xNaxNbO3based on the 8thorder polynomial function, and then establish the temperature-misfit strain and out-of-plane stress-in-plane misfit strain phase diagrams and calculate electrocaloric (EC) entropy changes ΔSand temperature changes ΔT. This study focuses on mechanical and orientation controls of room-temperature EC effect of K0.5Na0.5NbO3films, which is critical for environmentally friendly electrocaloric refrigeration applications in practice. Under the stress-free and zero misfit strain conditions, the (111)-oriented K0.5Na0.5NbO3film in an electric field of 30 MV/m has a maximum EC ΔTof ~18 K near the rhombohedral ferroelectric-paraelectric phase transition temperature (about 673 K). However, an out-of-plane stress of about –6.7GPa can reduce the optimal operating temperature to room temperature where the K0.5Na0.5NbO3film has the EC ΔTof ~7.5 K under the action of applied electric field of 30 MV/m. The present work provides theoretical guidance for exploring the strain engineering and orientation engineering of K1–xNaxNbO3-based thin films with optimized electrocaloric and electromechanical properties.
INTERDISCIPLINARY PHYSICS AND RELATED AREAS OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
EDITOR'S SUGGESTION
2022, 71 (9): 098101.
doi:10.7498/aps.71.20211870
Abstract +
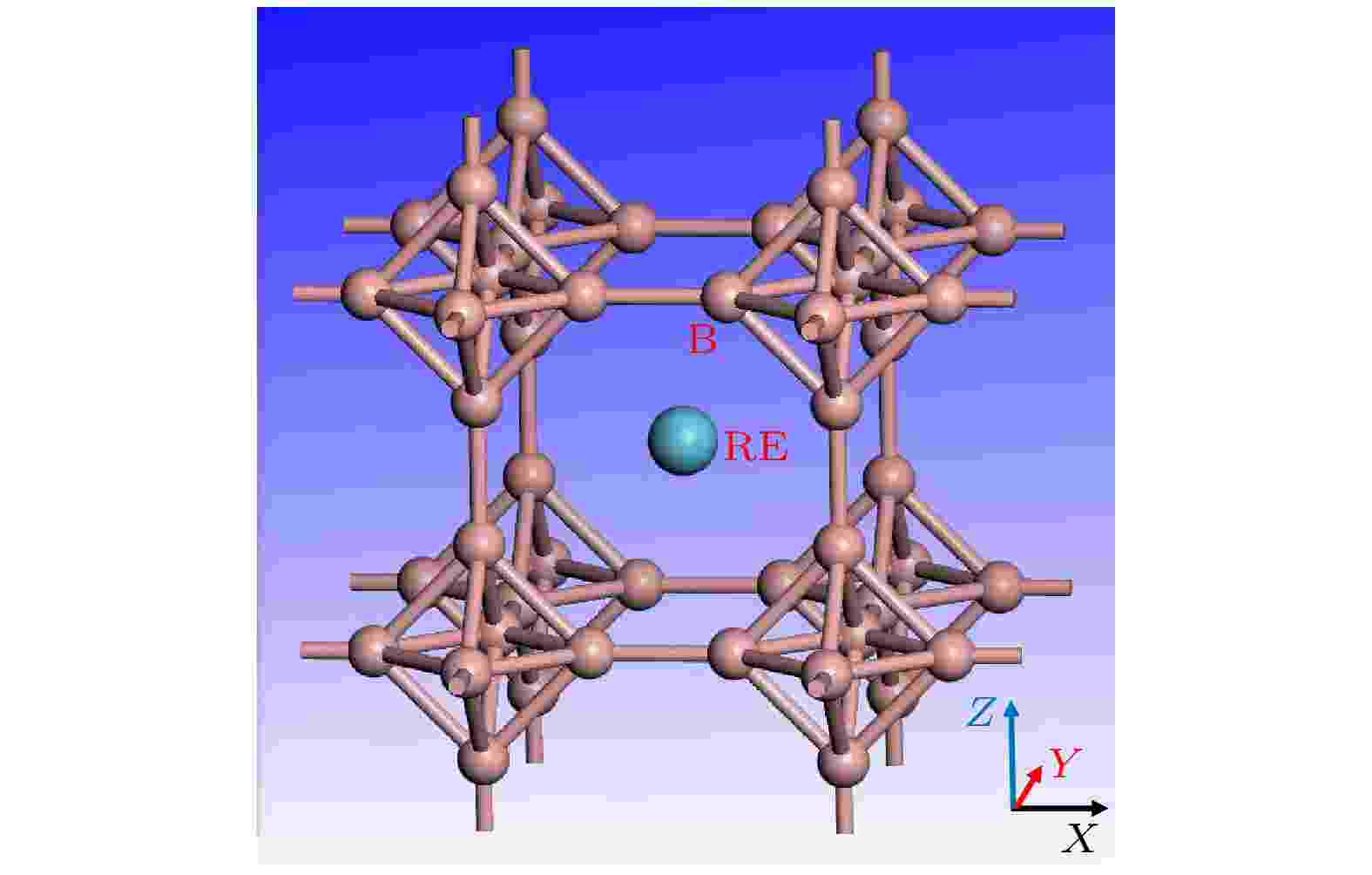
Binary rare earth hexaborides (REB6) have different rare earth elements with different valence electron distributions, which lead to different strange physical properties and different emission properties. However, in the electron emission properties, whether PrB6, NdB6, SmB6and GdB6all have excellent emission properties remains to be further studied, and the physical mechanism affecting their emission properties needs investigating. In this paper, the electronic structures, work functions of typical binary single crystal REB6(LaB6, CeB6, PrB6, NdB6, SmB6, GdB6) are studied by first principles calculations. The single crystal REB6are prepared by optical zone melting method, and their thermionic electron emission properties are tested experimentally. The theoretical calculation results show that the typical binary REB6have large densities of states near the Fermi level. The d-orbitals with broad distributions in conduction bands are beneficial to electron emission. The localized f-orbital electrons in valence bands are not conducive to their electron emission. The theoretical calculations of work functions of typical binary single crystal REB6(100) surface are consistent with the analyses of their electronic structures. The theoretical calculation values of work functions are ordered as GdB6(2.27 eV) < CeB6(2.36 eV) < LaB6(2.40 eV) < PrB6(2.58 eV) < SmB6(2.63 eV) < NdB6(2.91 eV). The experimental test results of thermionic electron emission of single crystal show that the experimental thermionic electron properties are consistent with the theoretical ones. The LaB6and CeB6both have good thermionic and field emission properties, and the GdB6has excellent field emission properties.
2022, 71 (9): 098201.
doi:10.7498/aps.71.20212148
Abstract +
Periodic forcing of pattern-forming systems is always a research hot spot in the field of pattern formation since it is one of the most effective methods of controlling patterns. In reality, most of the pattern-forming systems are the multilayered systems, in which each layer is a reaction-diffusion system coupled to adjacent layers. However, few researches on this issue have been conducted in the multilayered systems and their responses to the periodic forcing have not yet been well understood. In this work, the influences of the spatial periodic forcing on the Turing patterns in two linearly coupled layers described by the Brusselator (Bru) model and the Lengyel-Epstein (LE) model respectively have been investigated by introducing a spatial periodic forcing into the LE layer. It is found that the subcritical Turing mode in the LE layer can be excited as long as one of the external spatial forcing and the supercritical Turing mode (referred to as internal forcing mode) of the Bru layer is a longer wave mode. These three modes interact together and give rise to complex patterns with three different spatial scales. If both the spatial forcing mode and the internal forcing mode are the short wave modes, the subcritical Turing mode in the LE layer cannot be excited. But the superlattice pattern can also be generated when the spatial resonance is satisfied. When the eigenmode of the LE layer is supercritical, a simple and robust hexagon pattern with its characteristic wavelength appears and responds to the spatial forcing only when the forcing intensity is large enough. It is found that the wave number of forcing has a powerful influence on the spatial symmetry of patterns.
2022, 71 (9): 098301.
doi:10.7498/aps.71.20211954
Abstract +
The effect of temperature on the lattice constants of martensite and ferrite are studied by the synchrotron radiation technique. The results show that the lattice constants of martensite and ferrite increase gradually with the increase of temperature, but diffraction peaks of martensite show a peak splitting phenomenon, while the diffraction peaks of ferrite do not. From the fitting of the {110} and {200} diffraction peaks of martensite, it is found that the lattice constantsaandcof martensite gradually increase with the temperature rising, but the increasing rate of lattice constantais faster than that ofc, that is, the squareness of martensite gradually decreases. When the temperature increases to 500 ℃, the squareness (c/a) of martensite is equal to 1. The variation of lattice constant of ferrite with temperature is basically the same as that of lattice constantaof martensite, but different from that of lattice constantcof martensite, showing the nature influence of temperature on the lattice constants of martensite. Besides, based on the analysis of synchrotron radiation data, the quantitative equations of lattice constants of martensite and ferrite varying with temperature are established.
GEOPHYSICS, ASTRONOMY, AND ASTROPHYSICS
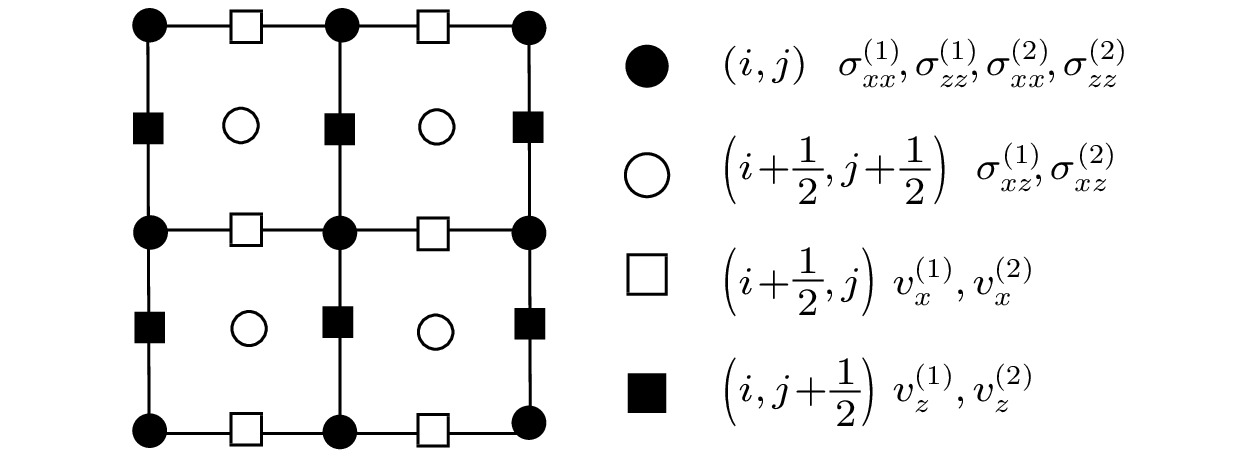
2022, 71 (9): 099101.
doi:10.7498/aps.71.20212012
Abstract +
Aiming at the propagation characteristics of acoustic waves in a porous medium containing a solid in pores, the equations of motion and constitutive relation are deducted in the case of two-solid porous media. The frequency dispersion and attenuation characteristics of wave modes are analyzed by a plane wave analysis. In addition, based on the first-order velocity-stress equations, the time-splitting high-order staggered-grid finite-difference algorithm is proposed and constructed for understanding wave propagation mechanisms in such a medium, where the time-splitting method is used to solve the stiffness problem in the first-order velocity-stress equations. The generation mechanisms and energy distributions of different kinds of waves are investigated in detail. In particular, the influences of the friction coefficient between solid grains and pore solid as well as frequency on wave propagation are analyzed. It can be known from the results of plane wave analysis that there are two compression waves (P1 and P2) and two shear waves (S1 and S2) in a porous medium containing a solid in pores. The attenuations of P2 wave and S2 wave are much larger than those of P1 wave and S1 wave. This is due to the friction between the solid grains and the pore solid. The results show that our proposed numerical simulation algorithm can effectively solve the problem of stiffness in the velocity-stress equations, with high accuracy. The excitation mechanisms of the four wave modes are clearly revealed by the simulation results. The P1 wave and S1 wave propagate primarily in the solid grain frame, while P2 wave and S2 wave are concentrated mainly in the pore solid, which are caused by the relative motion between the solid grains and the pore solid. Besides, it should be pointed out that the wave diffusions of the P2 wave and S2 wave are influenced by the friction coefficient between solid grains and pore solid. The existence of friction coefficient between two solids makes P2 wave and S2 wave attenuate to a certain extent at high frequency, but the attenuation is much smaller than that at low frequency. This is the reason why it is difficult to observe the slow waves in practice. However, because the slow waves also carry some energy, it may not be ignored in the studying of the energy attenuation of acoustic waves in porous media.















