Most Cited
2023, 72 (1): 018401.
doi:10.7498/aps.72.20222012
Abstract +
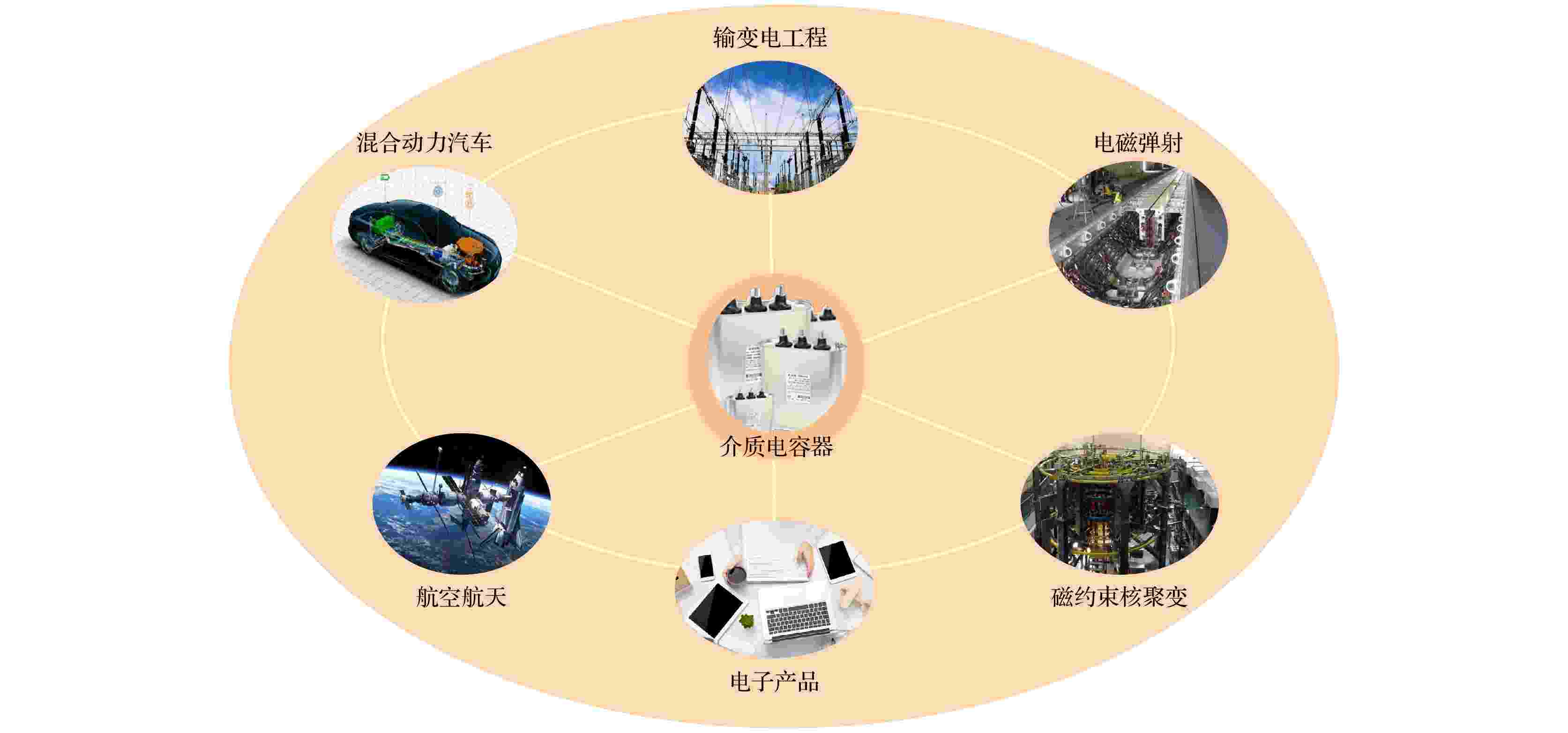
Dielectric capacitors have been widely used in crucial energy storage systems of electronic power systems because of their advantages such as fast charge discharge rates, long cycle lifetimes, low losses, and flexible and convenient processingc. However, the dielectric capacitors have lower energy storage densities than electrochemical energy storage devices, which makes them difficult to meet higher application requirements for electrical engineering at the present stage. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) based polymers show great potential in achieving improved energy storage properties, which is attributed to their high dielectric constants and high breakdown strengths. This work systematically reviews PVDF-based nanocomposites for energy storage applications. Dielectric constant, breakdown strength and charge discharge efficiency are three main parameters related to energy storage properties, which are proposed to discuss their mechanisms of action and optimization strategies. Finally, the key scientific problems of PVDF-based high energy storage composites are summarized and considered, and the future development trend of dielectric capacitors is also prospected.
2023, 72 (5): 057503.
doi:10.7498/aps.72.20221997
Abstract +
In recent years, with the rapid development of the emerging technologies including the internet of things, cloud computing, big data, and artificial intelligence, higher computing capability is required. Traditional semiconductor devices are confronting huge challenges brought by device miniaturization, energy consumption, heat dissipation, etc. Moore’s law which succeeds in guiding downscaling and upgrading of microelectronics is nearing its end. A new information carrier, instead of electrons, is required urgently for information transmission and processing. Spin waves are collectively excited waves in ordered magnets, and the quantized quasi particle is referred to as magnon. The propagation of magnons does not involve electron motion and produces no Joule heating, which can solve the increasing significant issues of heating dissipation in electronic devices. Thus, magnon-based devices have important application prospects in low-power information storage and computing. In this review, we first introduce the recent advances in the excitation, propagation, manipulation, detection of spin waves and magnon-based devices. Then, we mainly discuss the researches of our group. This part is described from four aspects: 1) Chiral magnonics, including the chiral propagarion of magnetostatic spin waves, Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction(DMI)-induced nonreciprocity of spin waves, spin-wave propagation at chiral interface, magnonic Goos-Hänchen effect, spin-wave lens, and magnonic Stern-Gerlach effect; 2) nonlinear magnonics, including three-magnon processes induced by DMI and noncollinear magnetic textures, skyrmion-induced magnonic frequency comb, twisted magnon frequency comb, and Penrose superradiance; 3) topological magnonics, including magnon Hall effect, magnonic topological insulator, magnonic topological semimetal, topological edge states and high-order corner states of magnetic solitons arranged in different crystal lattices; 4) quantum magnonics, including quantum states of magnon, magnon-based hybrid quantum systems, and cavity magnonics. Finally, the future development and prospect of magnonics are analyzed and discussed.
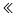
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- ...
- 16
- 17