-
针对复杂网络中关键节点的识别、评估及排序问题, 受物理系统中不同节点间信息的多维度、多层次相互影响过程的启发, 提出了一种基于图卷积神经网络的多维参数的节点重要性评估方法. 该方法结合了卷积神经网络自动学习的特性, 综合考虑节点的内在特性、与邻近节点的交互关系以及其在整个网络中的功能角色, 构建了一种新颖的关键节点识别框架, 即多维参数控制图卷积网络(multi-parameter control graph convolutional networks, MPC-GCN). 通过卷积神经网络对节点及其邻居特征的逐层聚合, 自动提取并综合节点的局部特性、全局特性及位置特性, 实现对节点重要性的多维度评估, 同时引入灵活的参数调整机制, 允许调整不同维度信息对评估结果的影响权重, 以适应不同结构网络的需求. 为验证该方法的有效性, 在随机生成的小型网络上验证了参数对模型的作用; 并在8个大型网络上利用SIR模型进行仿真实验, 以 M( R)值、Kendall相关系数、被传染节点占比及最大连通子图相对大小作为评价标准. 结果表明, MPC-GCN方法在单调性、准确性、适用性及鲁棒性上都优于其他相关方法, 能够显著区分不同节点的重要程度. 该方法有效克服了现有方法在评估角度和适应能力上的局限性, 提高了评估的全面性和适用性.This paper deals with the problem of identifying, evaluating, and ranking key nodes in complex networks by introducing a novel multi-parameter control graph convolutional network (MPC-GCN) for assessing node importance. Drawing inspiration from the multidimensional and hierarchical interactions between nodes in physical systems, this method integrates the automatic feature learning capabilities of graph convolutional networks (GCNs) with a comprehensive analysis of intrinsic properties of nodes, their interactions with neighbors, and their roles in the broader network. The MPC-GCN model provides an innovative framework for identifying key node by using GCNs to iteratively aggregate node and neighbor features across layers. This process captures and combines local, global, and positional characteristics, enabling a more nuanced, multidimensional assessment of node importance. Moreover, the model also includes a flexible parameter adjustment mechanism that allows for adjusting the relative weights of different dimensions, thereby adapting the evaluation process to various network structures. To validate the effectiveness of the model, we first test the influence of model parameters on randomly generated small networks. We then conduct extensive simulations on eight large-scale networks by using the susceptible-infected-recovered (SIR) model. Evaluation metrics, including the M( R) score, Kendall’s tau correlation, the proportion of infected nodes, and the relative size of the largest connected component, are used to assess the model’s performance. The results demonstrate that MPC-GCN outperforms existing methods in terms of monotonicity, accuracy, applicability, and robustness, providing more precise differentiation of node importance. By addressing the limitations of current methods, such as their reliance on single-dimensional perspectives and lack of adaptability, the MPC-GCN provides a more comprehensive and flexible approach to node importance assessment. This method significantly improves the breadth and applicability of node ranking in complex networks.
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] [10] [11] [12] [13] [14] [15] [16] [17] [18] [19] [20] [21] [22] [23] [24] [25] [26] [27] [28] [29] [30] [31] [32] [33] [34] [35] [36] [37] [38] [39] [40] [41] [42] [43] [44] [45] -
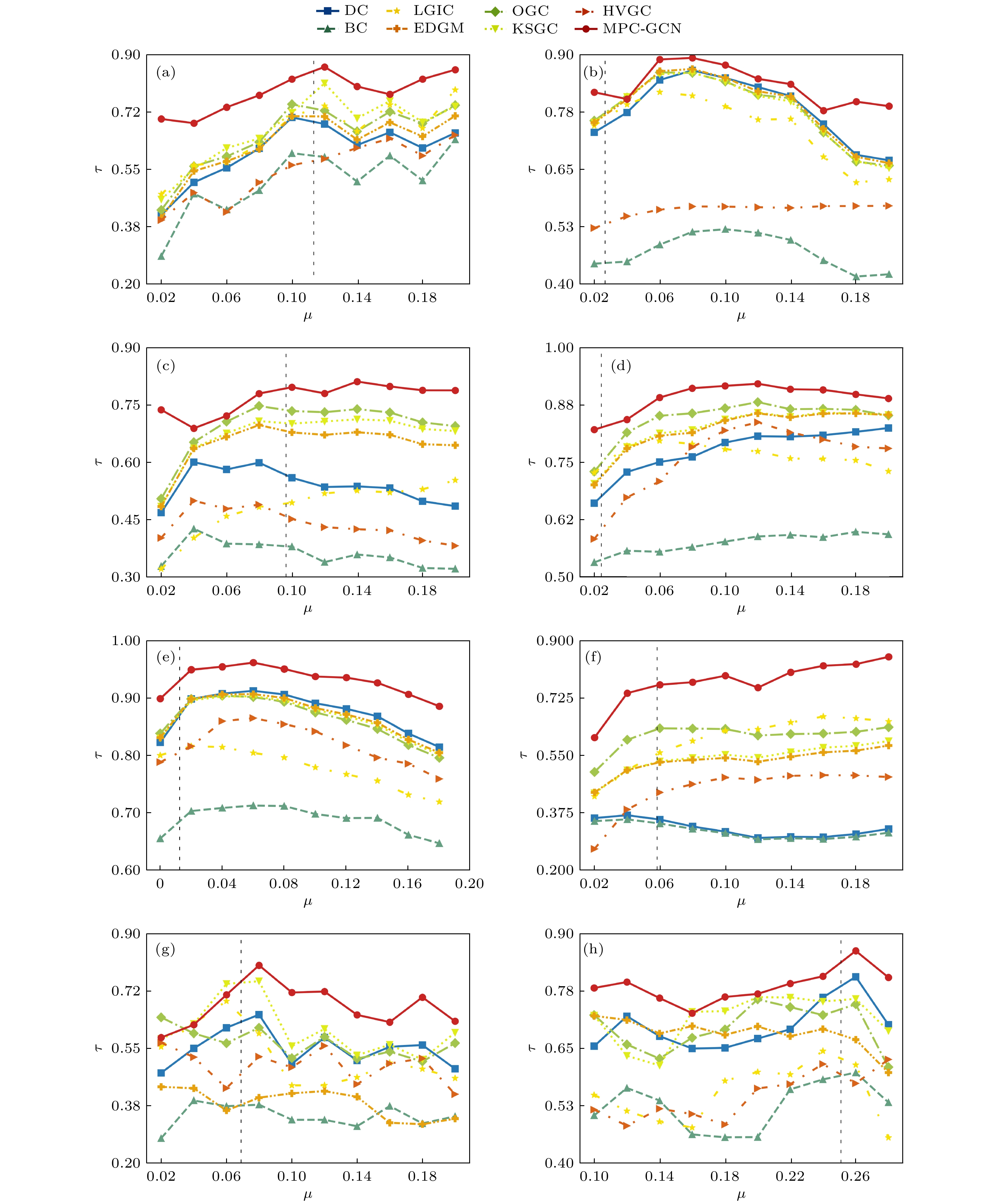
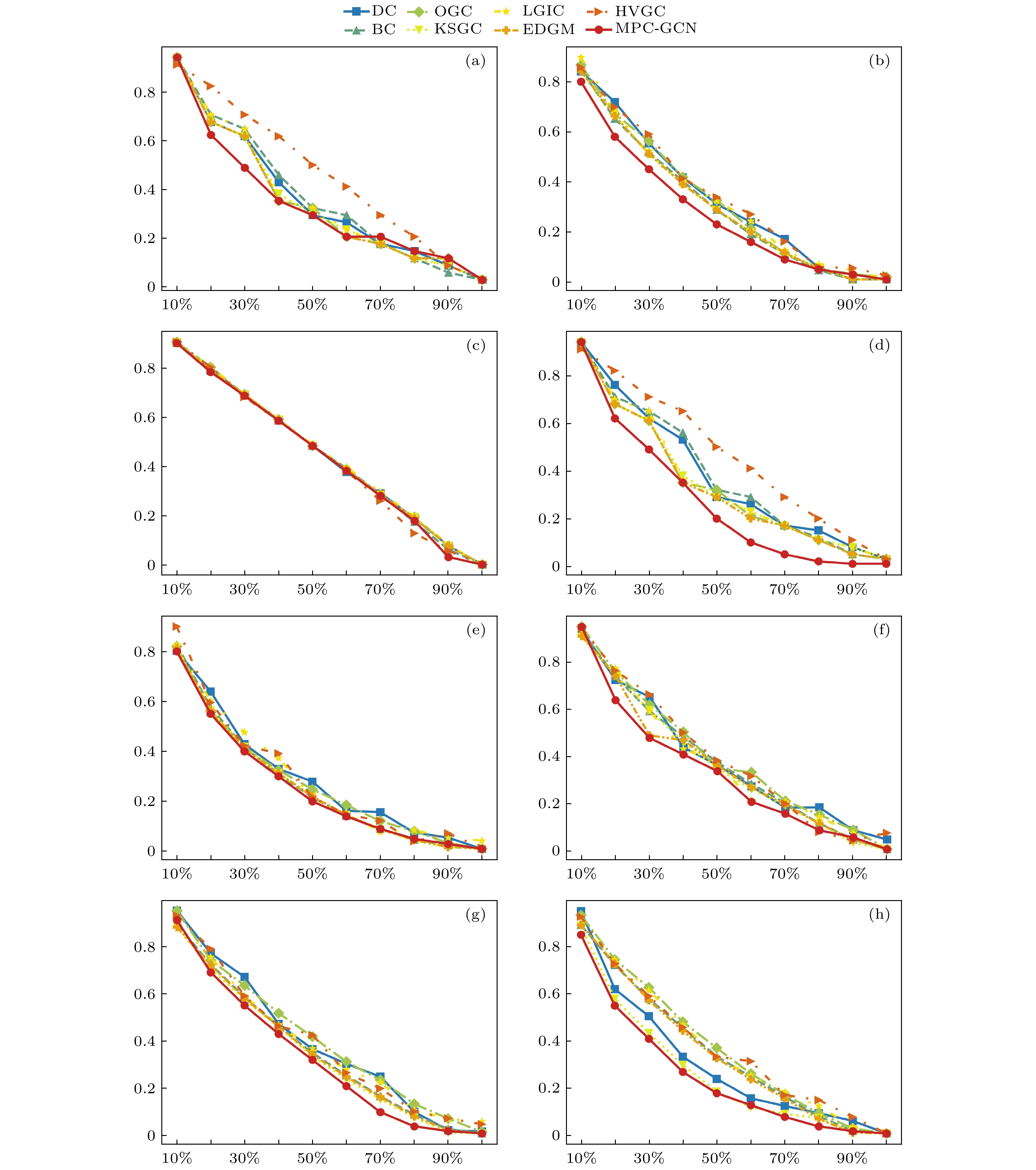
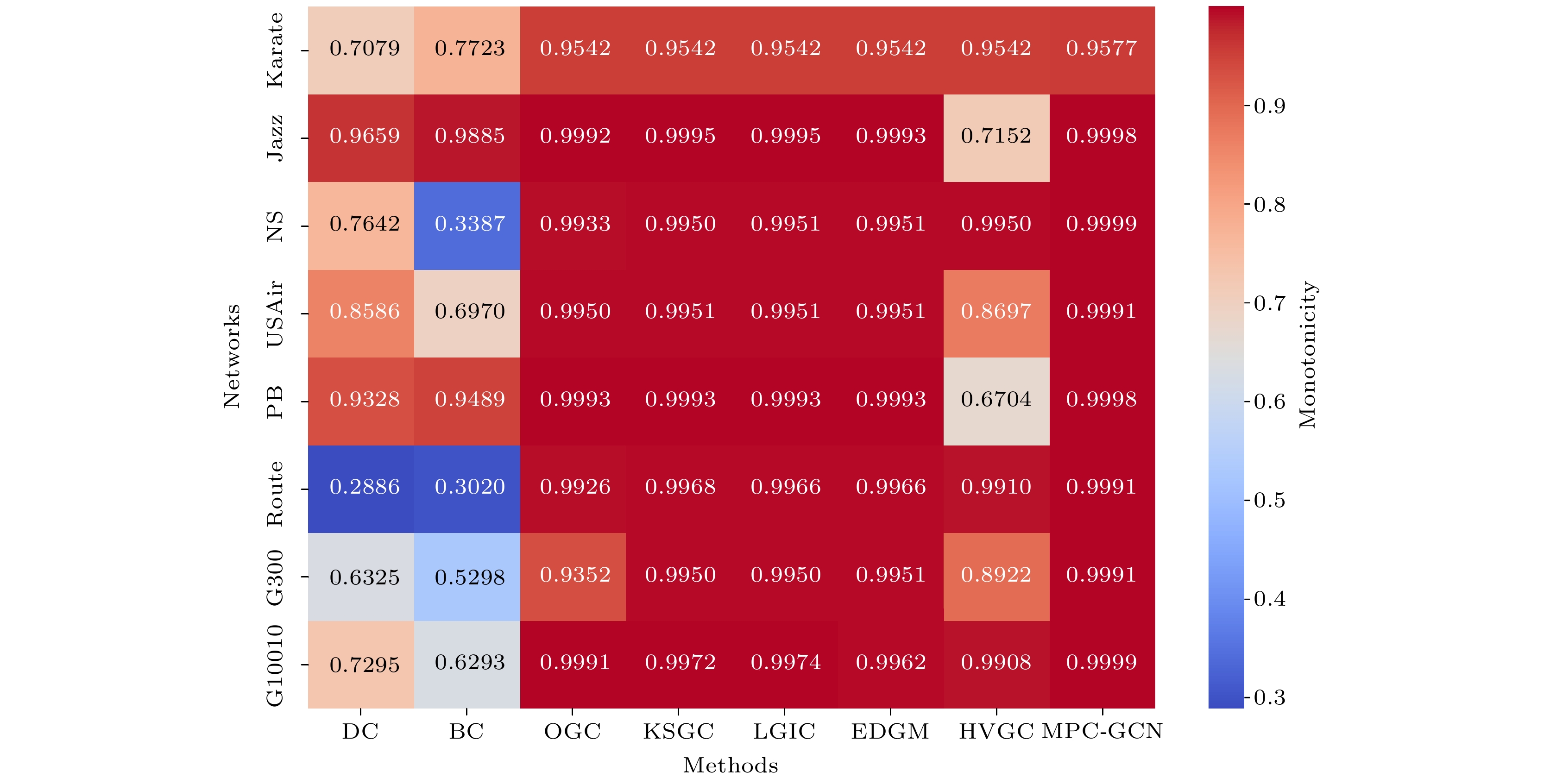
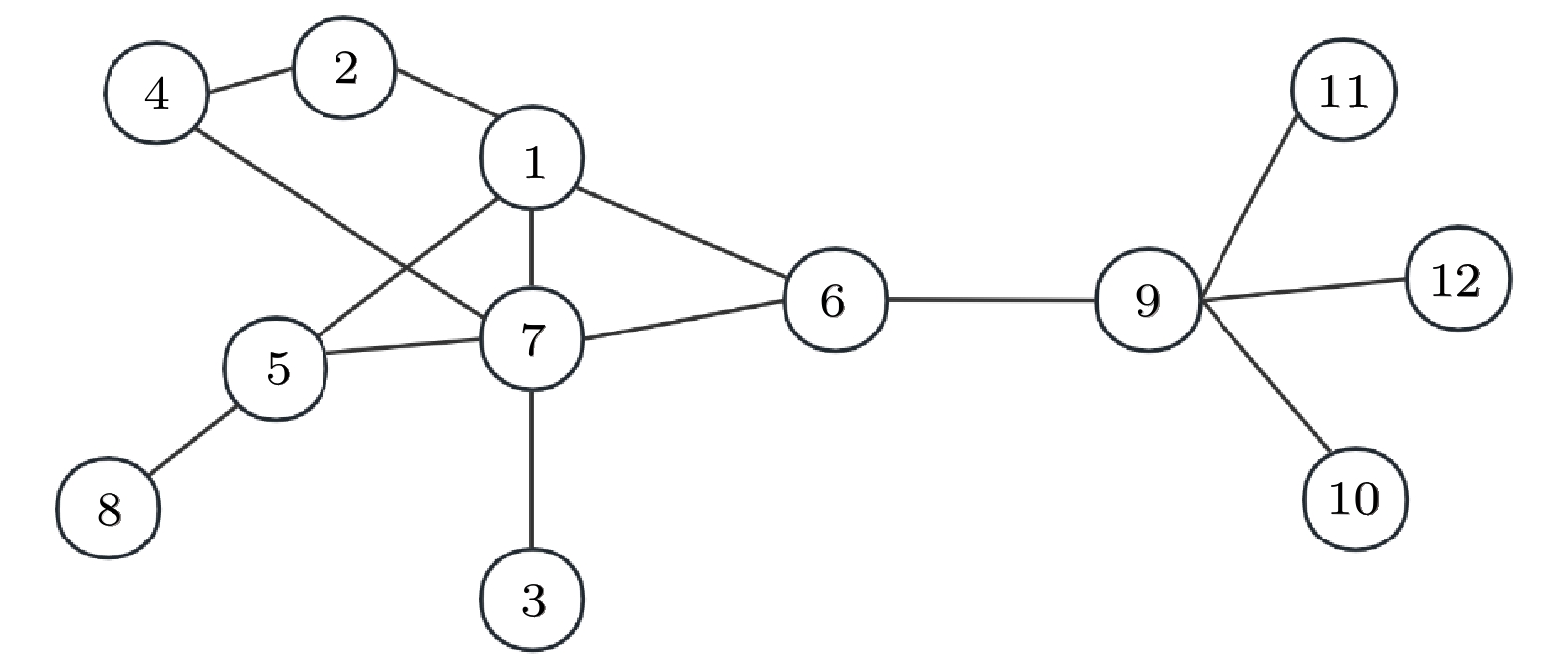
网络 V E $ \left\langle k \right\rangle $ $ {k_{\max }} $ $ \left\langle d \right\rangle $ $ {d_{\max }} $ $ {\mu _{{\text{th}}}} $ D C Karate 33 54 6.5455 22 1.9924 4 0.1134 0.14 0.57 Jazz 198 2742 27.6970 100 2.2350 6 0.0266 0.14 0.62 NS 379 914 4.8232 34 6.0419 17 0.0964 0.013 0.74 USAir 332 2126 12.8072 139 2.7381 6 0.0243 0.039 0.63 PB 1222 16714 27.3552 351 2.7375 8 0.0125 0.022 0.32 Router 5022 6258 2.49 106 6.4488 15 0.0583 0.00050 0.012 G300 300 2218 14.79 27 2.41 4 0.069 0.050 0.050 G10010 10010 19891 3.97 13 17.32 109 0.251 0.00040 0.00023 名称 SIR DC BC OGC KSGC LGIC EDGM HVGC MPC-GCN 排序结果 7 7 6 7 7 7 7 7 7 1 9 9 1 9 1 1 9 1 6 1 7 6 1 6 6 1 6 2 6 5 2 6 2 2 6 2 5 5 1 5 5 5 5 5 5 4 2 2 9 2 9 9 2 4 9 4 12 4 4 4 4 4 9 3 12 11 3 3 3 3 3 3 8 11 10 8 8 12 12 8 8 11 10 8 12 12 11 11 12 10 10 8 4 11 11 10 10 11 12 12 3 3 10 10 8 8 10 11 τ –0.606 –0.0303 0.667 0.333 0.576 0.576 0.333 0.939 网络 δ 拟合优度检验 P值 <0.05 λ 拟合优度检验 P值 <0.05 Karate 0.55 0.29 否 4.59 6.28×102 是 Jazz 0.27 0.15 是 27.70 2.89×1023 是 NS 1.55 0.76 是 4.82 5.61×1014 是 USAir 0.95 0.77 是 12.81 1.22×108 是 PB 1.07 0.85 是 27.36 1.07×10247 是 Router 1.77 0.89 是 2.49 2.31×10125 是 G300 0.79 0.073 否 14.79 14.51 否 G10010 0.24 0.054 否 4.04 29.6 否 -
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] [10] [11] [12] [13] [14] [15] [16] [17] [18] [19] [20] [21] [22] [23] [24] [25] [26] [27] [28] [29] [30] [31] [32] [33] [34] [35] [36] [37] [38] [39] [40] [41] [42] [43] [44] [45]
计量
- 文章访问数:305
- PDF下载量:6
- 被引次数:0













 下载:
下载: