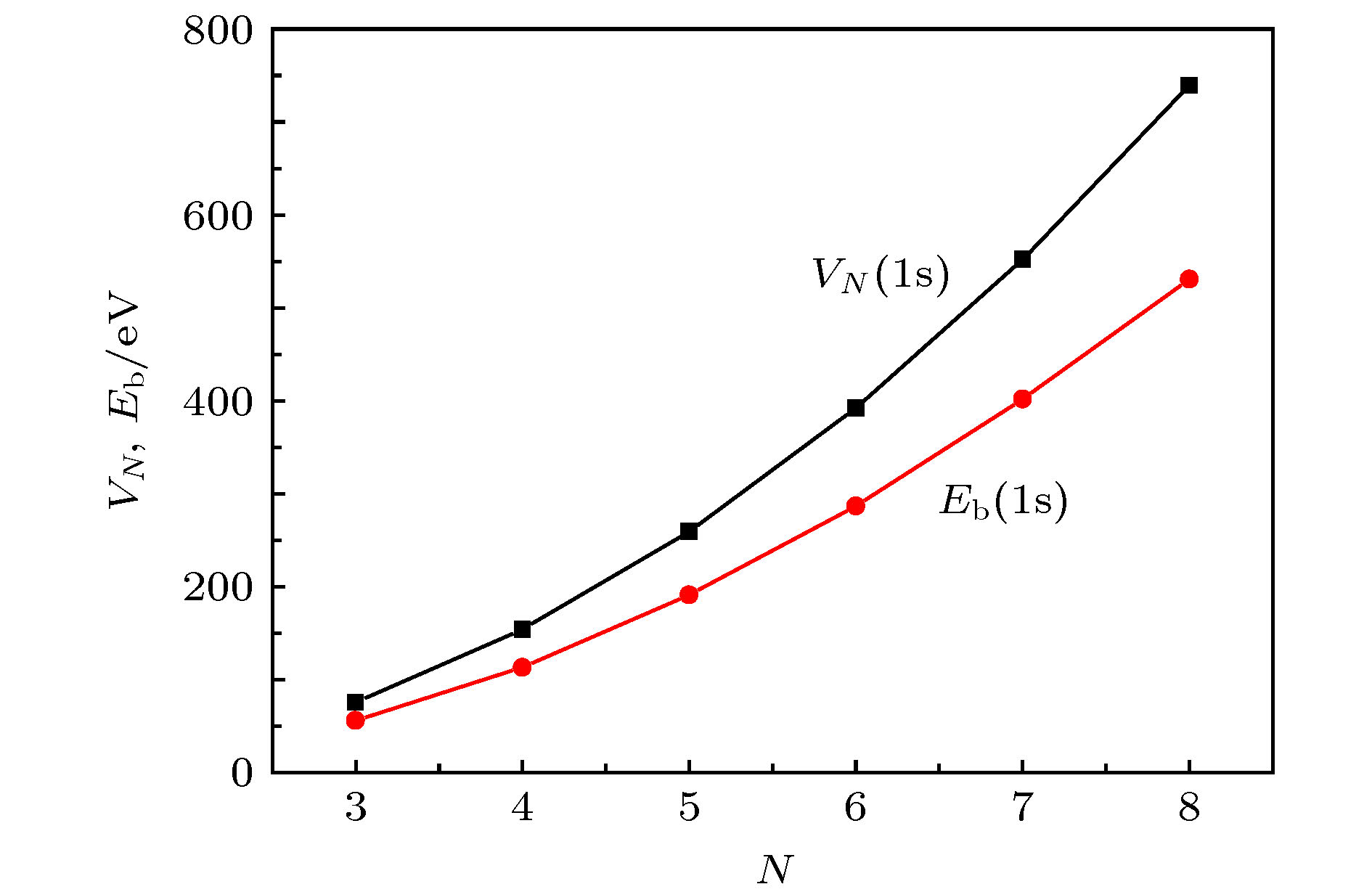
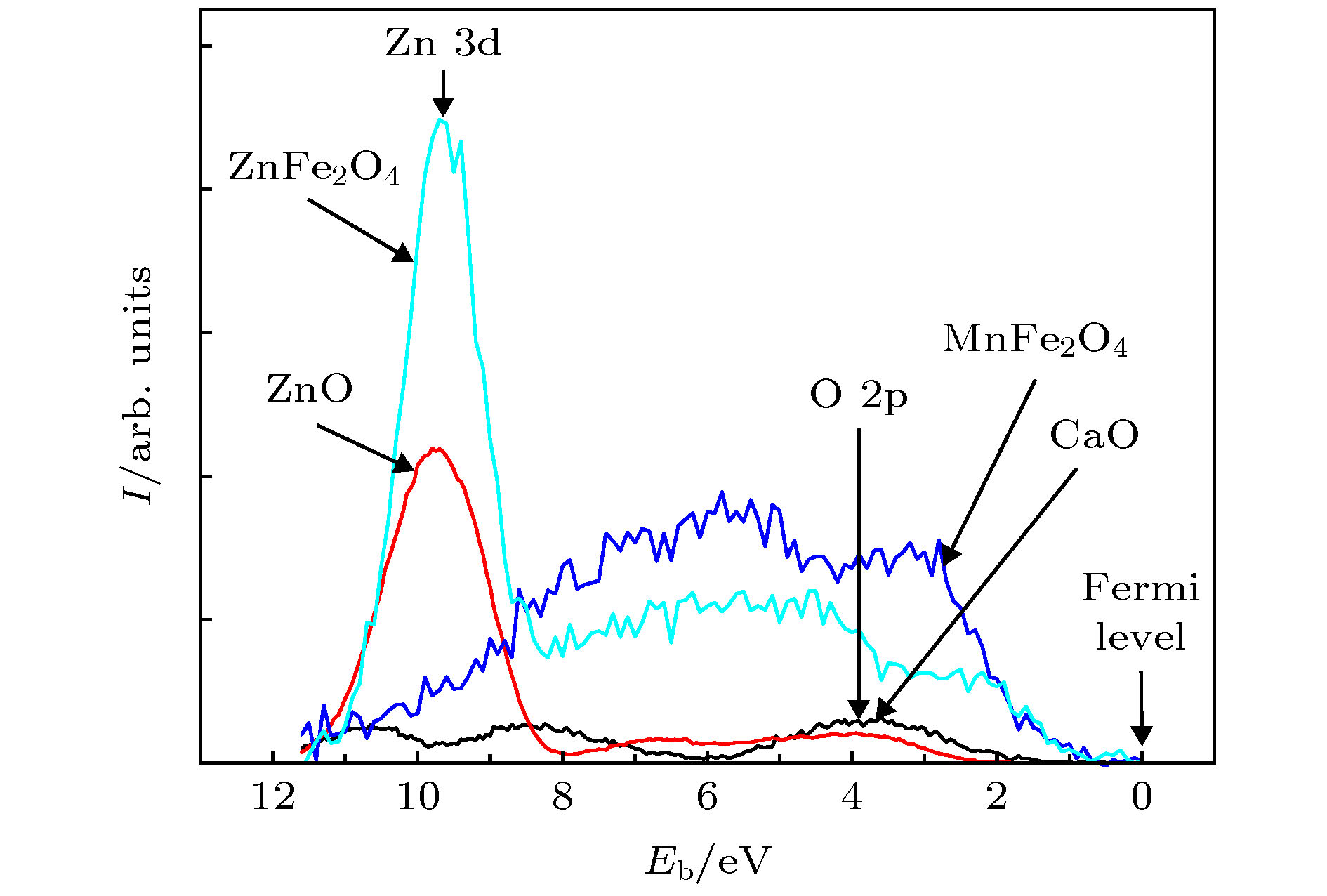
The conventional magnetic ordering models, exchange interaction, super-exchange (SE) interaction and double exchange (DE) interaction models relating to the valence electron structure in the materials, were proposed about in or before the 1950's, the time when there was little experimental evidence. Since the 1970's, more and more experimental results for the valence electron states have been reported. These experimental results suggested that the conventional magnetic ordering models need improving. i) Many experimental results, including the electron energy-loss spectra (EELS), X-ray absorption spectra (XAS), and X-ray photoelectron spectra (XPS), indicate that there are O
–anions in addition to O
2–anions in oxides, and that the percentage of O
–anions may reach 30% or more. This suggests that the SE model and DE model both need to improving, in which all oxygen anions are assumed to be O
2–anions. ii) Several experimental results, including gamma radiation diffraction, XAS and magnetic circular dichroism spectra (XMCD), suggest that part of 4s electrons enter into 3d orbits and transit into the 3d electrons in the process of forming metals from free atoms. The effect of the orbital magnetic moment on the magnetic moment of a bulk metal is far smaller than the spin magnetic moments. These provide the evidence of exploring the relation between magnetic moment and electrical resistivity of the magnetic metal. iii) Using density function theory (DFT) to fit physical properties yields plenty of results for many materials, but there exist serious difficulties for magnetic materials. This is due to magnetic ordering energy is included in the exchange correlation energy, which has been find no phenomenological expression so far, and has to be fitted using various models in DFT calculation. These investigations provide an opportunity to improve magnetic ordering models. Therefore, our group proposed three models of magnetic ordering in typical magnetic materials, they including an O 2p itinerant electron model for magnetic oxides (IEO model), a new itinerant electron model for magnetic metal (IEM model), and a Weiss electron pair (WEP) model for the origin of magnetic ordering energy. Replacing the SE model and DE model with the IEO model, the magnetic structures of Co, Ni, Cu doped spinel ferrites as well as Cr and Ti doped spinel ferrites can be explained. The dependence of the magnetic moment on the Sr content in perovskite manganites La
1–xSr
xMnO
3can also be explained, for which there have been many ongoing disputes about the cation distributions. With the IEM model, we can explain qualitatively the relation of the magnetic moment with the resitivity for each of Fe, Co, Ni, Cu metals, and fit the curves of the resistivity of NiCu alloy versus test temperature and the Cu doped level. With the WEP model, we can explain why Fe, Co, Ni metal, NiCu alloys, Fe
3O
4and La
0.7Sr
0.3MnO
3oxides have different Curie temperature values. The new itinerant electron model is different from the classical model in the following three elementary characteristics. First, the s electrons in free 3d transition metal atoms are divided into two parts when they form a metal or alloy. One part of these s electrons enter into the d orbits and change into the d electrons. and the other part of those electrons are the free electrons which are no longer called the s electrons. Second, only the d electrons occupying the outer orbit of an ion core in a metal or alloy may form itinerant electrons with a certain probability, while the remaining d electrons are local electrons. Third, whether in a magnetic metal or in a magnetic oxide, the transition of the itinerant electrons is the spin-dependent transition below the Curie temperature, and the transition probability decreases with test temperature increasing. The transition of the itinerant electrons turns into the spin-independent transition when the temperature is above the Curie temperature. In this paper, first, we introduce several typical experimental results of the valence electron states. Then, we present the new magnetic ordering models proposed by our group and analyze the elementary differences between the new models and the conventional models. Finally, we point out the challenge to the future work.













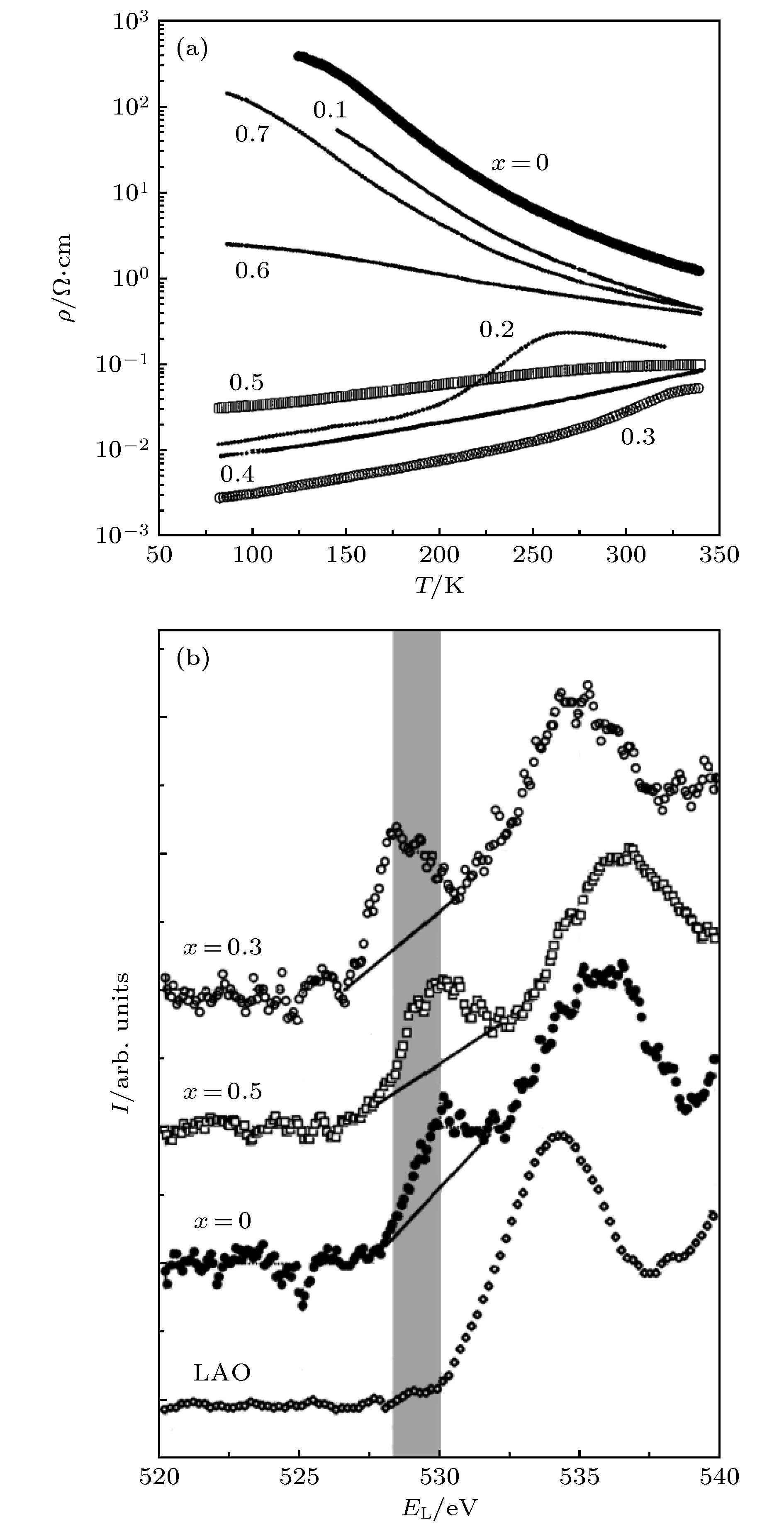
 下载:
下载: